Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the angle of contact.
उत्तर
When a liquid is in contact with a solid, the angle between the tangent drawn to the free surface of the liquid and the surface of the solid at the point of contact measured inside the liquid is called the angle of contact.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for excess pressure inside a drop of liquid.
A raindrop of diameter 4 mm is about to fall on the ground. Calculate the pressure inside the raindrop. [Surface tension of water T = 0.072 N/m, atmospheric pressure = 1.013 x 105 N/m2 ]
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing forces acting on the meniscus of water in a capillary tube.
Explain why Surface tension of a liquid is independent of the area of the surface
Explain why Water with detergent dissolved in it should have small angles of contact.
Fill in the blanks using the word(s) from the list appended with each statement
Surface tension of liquids generally . . . with temperatures (increases / decreases)
What is the excess pressure inside a bubble of soap solution of radius 5.00 mm, given that the surface tension of soap solution at the temperature (20 °C) is 2.50 × 10–2 N m–1? If an air bubble of the same dimension were formed at depth of 40.0 cm inside a container containing the soap solution (of relative density 1.20), what would be the pressure inside the bubble? (1 atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 105 Pa).
Show that the surface tension of a liquid is numerically equal to the surface energy per unit
area.
State any two characteristics of the angle of contact
If a mosquito is dipped into water and released, it is not able to fly till it is dry again. Explain
Frictional force between solids operates even when they do not move with respect to each other. Do we have viscous force acting between two layers even if there is no relative motion?
An ice cube is suspended in vacuum in a gravity free hall. As the ice melts it
When water droplets merge to form a bigger drop
Air is pushed into a soap bubble of radius r to double its radius. If the surface tension of the soap solution in S, the work done in the process is
Which of the following graphs may represent the relation between the capillary rise hand the radius r of the capillary?
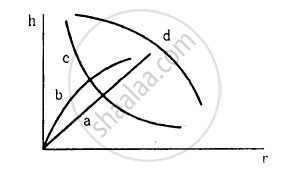
Water rises in a vertical capillary tube up to a length of 10 cm. If the tube is inclined at 45°, the length of water risen in the tube will be
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
The contact angle between a solid and a liquid is a property of
(a) the material of the solid
(b) the material of the liquid
(c) the shape of the solid
(d) the mass of the solid
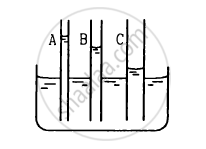
The capillaries shown in figure have inner radii 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm respectively. The liquid in the beaker is water. Find the heights of water level in the capillaries. The surface tension of water is 7.5 × 10−2 N m−1.
The lower end of a capillary tube is immersed in mercury. The level of mercury in the tube is found to be 2 cm below the outer level. If the same tube is immersed in water, up to what height will the water rise in the capillary?
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius 1.0 mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to 76 cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass = 135° and surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1. Density of mercury = 13600 kg m−3.
A capillary tube of radius 0.50 mm is dipped vertically in a pot of water. Find the difference between the pressure of the water in the tube 5.0 cm below the surface and the atmospheric pressure. Surface tension of water = 0.075 N m−1.
The lower end of a capillary tube of radius 1 mm is dipped vertically into mercury. (a) Find the depression of mercury column in the capillary. (b) If the length dipped inside is half the answer of part (a), find the angle made by the mercury surface at the end of the capillary with the vertical. Surface tension of mercury = 0.465 N m−1 and the contact angle of mercury with glass −135 °.
A metal piece of mass 160 g lies in equilibrium inside a glass of water. The piece touches the bottom of the glass at a small number of points. If the density of the metal is 8000 kg/m3, find the normal force exerted by the bottom of the glass on the metal piece.

A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in K.oil (in the following figure). Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in K.oil. Specific gravity of K.oil is 0.8 and that of ice is 0.9.

A cubical metal block of edge 12 cm floats in mercury with one fifth of the height inside the mercury. Water in it. Find the height of the water column to be poured.
Specific gravity of mercury = 13.6.
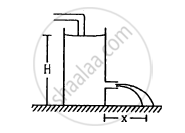
Water level is maintained in a cylindrical vessel up to a fixed height H. The vessel is kept on a horizontal plane. At what height above the bottom should a hole be made in the vessel so that the water stream coming out of the hole strikes the horizontal plane at the greatest distance from the vessel.
The energy stored in a soap bubble of diameter 6 cm and T = 0.04 N/m is nearly ______.
Insect moves over the surface of water because of ______.
Define surface tension
What will be the shape of the liquid meniscus for the obtuse angle of contact?
Numerical Problem.
A stone weighs 500 N. Calculate the pressure exerted by it if it makes contact with a surface of area 25 cm2.
Describe an experiment to prove that friction depends on the nature of a surface.
A certain number of spherical drops of a liquid of radius R coalesce to form a single drop of radius R and volume V. If T is the surface tension of the liquid, then
How is surface tension related to surface energy?
What are the factors affecting the surface tension of a liquid?
Obtain an expression for the excess of pressure inside a
- liquid drop
- liquid bubble
- air bubble
Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by the capillary rise method.
Why coffee runs up into a sugar lump (a small cube of sugar) when one corner of the sugar lump is held in the liquid?
The surface tension of the two liquids is respectively 20 and 60 dyne cm-1. The liquids drop from the ends of two tubes of the same radius. The ratio of the weights of the two drops is ______
Two small drops of mercury each of radius 'R' coalesce to form a large single drop. The ratio of the total surface energies before and after the change is ____________.
Water rises upto a height h in a capillary tube on the surface of the earth. The value of h will increase, if the experimental setup is kept in [g = acceleration due to gravity]
Under isothermal conditions, two soap bubbles of radii 'r1' and 'r2' coalesce to form a big drop. The radius of the big drop is ______.
The sap in trees, which consists mainly of water in summer, rises in a system of capillaries of radius r = 2.5 × 10–5 m. The surface tension of sap is T = 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and the angle of contact is 0°. Does surface tension alone account for the supply of water to the top of all trees?
Two mercury droplets of radii 0.1 cm. and 0.2 cm. collapse into one single drop. What amount of energy is released? The surface tension of mercury T = 435.5 × 10–3 Nm–1.
The sufrace tension and vapour pressure of water at 20°C is 7.28 × 10–2 Nm–1 and 2.33 × 103 Pa, respectively. What is the radius of the smallest spherical water droplet which can form without evaporating at 20°C?
Two narrow bores of diameter 5.0 mm and 8.0 mm are joined together to form a U-shaped tube open at both ends. If this U-tube contains water, what is the difference in the level of the two limbs, of the tube?
[Take surface tension of water T = 7.3 × 10-2 Nm-1, angle of contact = 0, g = 10 ms-2 and density of water = 1.0 × 103 kgm-3]
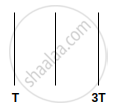
We have three identical perfectly black plates. The temperatures of first and third plate is T and 3T. What is the temperature of second plate if system is in equilibrium?
A drop of water and a soap bubble have the same radii. Surface tension of soap solution is half of that of water. The ratio of excess pressure inside the drop and bubble is ______.
A liquid drop of density ρ is floating half immersed in a liquid of density d. The diameter of the liquid drop is ______.
(ρ > d, g = acceleration due to gravity, T = surface tension)
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
A drop of water of radius 8 mm breaks into number of droplets each of radius 1 mm. How many droplets will be formed?
Define angle of contact.
