Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose focus is (2, −1), directrix is 2x + 3y = 1 and eccentricity = 2 .
उत्तर
Let S be the focus and
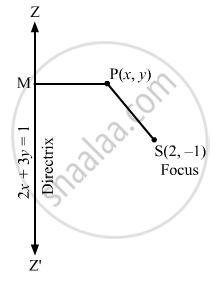
By definition:
SP = ePM
= ePM
Squaring both the sides:
∴ Equation of the hyperbola =
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given conditions:
Vertices (0, ±5), foci (0, ±8)
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given conditions:
Vertices (0, ±3), foci (0, ±5)
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given conditions:
Foci (0, ±13), the conjugate axis is of length 24.
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given conditions:
Foci
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose focus is (0, 3), directrix is x + y − 1 = 0 and eccentricity = 2 .
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose focus is (a, 0), directrix is 2x − y + a = 0 and eccentricity =
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose focus is (2, 2), directrix is x + y = 9 and eccentricity = 2.
Find the eccentricity, coordinates of the foci, equation of directrice and length of the latus-rectum of the hyperbola .
4x2 − 3y2 = 36
Find the eccentricity, coordinates of the foci, equation of directrice and length of the latus-rectum of the hyperbola .
2x2 − 3y2 = 5.
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose vertices are at (± 6, 0) and one of the directrices is x = 4.
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose foci at (± 2, 0) and eccentricity is 3/2.
If P is any point on the hyperbola whose axis are equal, prove that SP. S'P = CP2.
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given condition :
vertices (± 2, 0), foci (± 3, 0)
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given condition :
vertices (0, ± 5), foci (0, ± 8)
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given condition :
vertices (0, ± 3), foci (0, ± 5)
Find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given condition :
foci (0, ± 13), conjugate axis = 24
find the equation of the hyperbola satisfying the given condition:
vertices (± 7, 0),
Write the equation of the hyperbola whose vertices are (± 3, 0) and foci at (± 5, 0).
Equation of the hyperbola whose vertices are (± 3, 0) and foci at (± 5, 0), is
The foci of the hyperbola 2x2 − 3y2 = 5 are
Find the equation of the hyperbola with vertices at (0, ± 6) and e =
Find the equation of the hyperbola whose vertices are (± 6, 0) and one of the directrices is x = 4.
The length of the transverse axis along x-axis with centre at origin of a hyperbola is 7 and it passes through the point (5, –2). The equation of the hyperbola is ______.
If the distance between the foci of a hyperbola is 16 and its eccentricity is
Show that the set of all points such that the difference of their distances from (4, 0) and (– 4, 0) is always equal to 2 represent a hyperbola.
Find the equation of the hyperbola with vertices (0, ± 7), e =
Find the equation of the hyperbola with foci
The eccentricity of the hyperbola whose latus rectum is 8 and conjugate axis is equal to half of the distance between the foci is ______.
The distance between the foci of a hyperbola is 16 and its eccentricity is
Equation of the hyperbola with eccentricty
