Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Five forces \[\overrightarrow{AB,} \overrightarrow { AC,} \overrightarrow{ AD,}\overrightarrow{AE}\] and \[\overrightarrow{AF}\] act at the vertex of a regular hexagon ABCDEF. Prove that the resultant is 6 \[\overrightarrow{AO,}\] where O is the centre of hexagon.
उत्तर
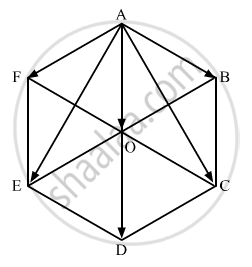
\[\overrightarrow{AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow{AD} + \overrightarrow{AE} + \overrightarrow{AF}\]
Consider ∆ADE,
\[\begin{array}{l}\overrightarrow{AD} + \overrightarrow{DE} + \overrightarrow{EA} = 0 \\ \overrightarrow{AD} + \overrightarrow{DE} = \overrightarrow{AE} \\ 2 \overrightarrow{AO} + \left( - \overrightarrow{AB} \right) =\overrightarrow{AE} \left[ \overrightarrow{AD} = 2 \overrightarrow{AO} \hspace{0.167em} \hspace{0.167em}\text{ and }ED ||\hspace{0.167em}AB \hspace{0.167em} \hspace{0.167em} \overrightarrow{DE} = - \overrightarrow{AB} \right] \\ \therefore \hspace{0.167em} \hspace{0.167em} \overrightarrow{AE} + \overrightarrow{AB} = 2 \overrightarrow{AO} . . . . . (1)\end{array}\]
Now, consider ∆ADC
\[\overrightarrow{AC} + \overrightarrow{CD} + \overrightarrow{DA} = 0\]
\[ \overrightarrow{AC} + \overrightarrow{CD} = \overrightarrow{AD} \left[ \because \overrightarrow{CD} = \overrightarrow{AF} \right]\]
\[ \overrightarrow{AC} + \overrightarrow{AF} = 2 \overrightarrow{AO} . . . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
Using (1) and (2),
\[\overrightarrow{AB} +\overrightarrow{AE} + \overrightarrow{AC} +\overrightarrow{AF}+\overrightarrow{AD} \]
\[ 2\overrightarrow{AO} + 2\overrightarrow{AO} + 2\overrightarrow{AO}\]
= \[6\overrightarrow{AO}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Classify the following measures as scalars and vectors:
(i) 15 kg
(ii) 20 kg weight
(iii) 45°
(iv) 10 meters south-east
(v) 50 m/sec2
Classify the following as scalars and vector quantities:
(i) Time period
(ii) Distance
(iii) displacement
(iv) Force
(v) Work
(vi) Velocity
(vii) Acceleration
Answer the following as true or false:
\[\vec{a}\] and \[\vec{a}\] are collinear.
Answer the following as true or false:
Two collinear vectors are always equal in magnitude.
If \[\vec{a}\] and \[\vec{b}\] are two non-collinear vectors having the same initial point. What are the vectors represented by \[\vec{a}\] + \[\vec{b}\] and \[\vec{a}\] − \[\vec{b}\].
If \[\vec{a}\] is a vector and m is a scalar such that m \[\vec{a}\] = \[\vec{0}\], then what are the alternatives for m and \[\vec{a}\] ?
If O is a point in space, ABC is a triangle and D, E, F are the mid-points of the sides BC, CA and AB respectively of the triangle, prove that \[\vec{OA} + \vec{OB} + \vec{OC} = \vec{OD} + \vec{OE} + \vec{OF}\]
If the vectors \[\vec{a} = 2 \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j}\] and \[\vec{b} = - 6 \hat{i} + m \hat{j}\] are collinear, find the value of m.
Show that the points A (1, −2, −8), B (5, 0, −2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC.
Using vectors show that the points A (−2, 3, 5), B (7, 0, −1) C (−3, −2, −5) and D (3, 4, 7) are such that AB and CD intersect at the point P (1, 2, 3).
If \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{b}\], \[\vec{c}\] are non-zero, non-coplanar vectors, prove that the following vectors are coplanar:
(1) \[5 \vec{a} + 6 \vec{b} + 7 \vec{c,} 7 \vec{a} - 8 \vec{b} + 9 \vec{c}\text{ and }3 \vec{a} + 20 \vec{b} + 5 \vec{c}\]
Prove that the following vectors are coplanar:
\[2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + \hat{k} , \hat{i} - 3 \hat{j} - 5 \hat{k} \text{ and }3 \hat{i} - 4 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k}\]
Prove that the following vectors are non-coplanar:
Prove that the following vectors are non-coplanar:
If \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{c}\] are non-coplanar vectors, prove that the following vectors are non-coplanar: \[2 \vec{a} - \vec{b} + 3 \vec{c} , \vec{a} + \vec{b} - 2 \vec{c}\text{ and }\vec{a} + \vec{b} - 3 \vec{c}\]
If \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{c}\] are non-coplanar vectors, prove that the following vectors are non-coplanar: \[\vec{a} + 2 \vec{b} + 3 \vec{c} , 2 \vec{a} + \vec{b} + 3 \vec{c}\text{ and }\vec{a} + \vec{b} + \vec{c}\]
Show that the vectors \[\vec{a,} \vec{b,} \vec{c}\] given by \[\vec{a} = \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} , \vec{b} = 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k}\text{ and }\vec{c} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k}\] are non coplanar.
Express vector \[\vec{d} = 2 \hat{i}-j- 3 \hat{k} , \text{ and }\text { as a linear combination of the vectors } \vec{a,} \vec{b}\text{ and }\vec{c} .\]
The vectors \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] satisfy the equations \[2 \vec{a} + \vec{b} = \vec{p} \text{ and } \vec{a} + 2 \vec{b} = \vec{q} , \text{ where } \vec{p} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} \text{ and } \vec{q} = \hat{i} - \hat{j} .\] the angle between \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] then
If \[\vec{a} \cdot \text{i} = \vec{a} \cdot \left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} \right) = \vec{a} \cdot \left( \hat{i} + \hat{j} + \hat{k} \right) = 1,\] then \[\vec{a} =\]
If \[\vec{a} + \vec{b} + \vec{c} = \vec{0} , \left| \vec{a} \right| = 3, \left| \vec{b} \right| = 5, \left| \vec{c} \right| = 7,\] then the angle between \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] is
If the position vectors of P and Q are \[\hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 7 \hat{k} \text{ and } 5 \text{i} - 2 \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\] then the cosine of the angle between \[\vec{PQ}\] and y-axis is
What is the length of the longer diagonal of the parallelogram constructed on \[5 \vec{a} + 2 \vec{b} \text{ and } \vec{a} - 3 \vec{b}\] if it is given that \[\left| \vec{a} \right| = 2\sqrt{2}, \left| \vec{b} \right| = 3\] and the angle between \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] is π/4?
If θ is the angle between two vectors `veca` and `vecb` then, `veca * vecb` ≥ 0, only when
If \[\vec{a} , \vec{b} , \vec{c}\] are any three mutually perpendicular vectors of equal magnitude a, then \[\left| \vec{a} + \vec{b} + \vec{c} \right|\] is equal to
If the vectors \[3 \hat{i} + \lambda \hat{j} + \hat{k} \text{ and } 2 \hat{i} - \hat{j} + 8 \hat{k}\] are perpendicular, then λ is equal to
The vectors \[2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k}\] and \[a \hat{i} + \hat{b} j + c \hat{k}\] are perpendicular if
If \[\left| \vec{a} \right| = \left| \vec{b} \right|, \text{ then } \left( \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right) \cdot \left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right) =\]
If \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] are unit vectors inclined at an angle θ, then the value of \[\left| \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right|\]
If the angle between the vectors \[x \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j}- 7 \hat{k} \text{ and } x \hat{i} - x \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k}\] is acute, then x lies in the interval
If \[\vec{a} \text{ and } \vec{b}\] are two unit vectors inclined at an angle θ, such that \[\left| \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right| < 1,\] then
If θ is an acute angle and the vector (sin θ) \[\text{i}\] + (cos θ) \[\hat{j}\] is perpendicular to the vector \[\hat{i} - \sqrt{3} \hat{j} ,\] then θ =
In Figure ABCD is a regular hexagon, which vectors are:
(i) Collinear
(ii) Equal
(iii) Coinitial
(iv) Collinear but not equal.
