Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How many faradays of electricity are required to produce 6 g of Mg from MgCl2?
उत्तर
Mg2+ + 2e- → Mg(s)
1 mole Mg2+ equals 2 mole e- for electrosis
1 mole Mg required 2 Faraday electricity
rquired 2 faraday electricity
6g Mg will require = `(2 xx 6)/24`
= 0.5 F
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can you store copper sulphate solutions in a zinc pot?
How many electrons flow through a metllic wire if a current of 0·5 A is passed for 2 hours? (Given : 1 F = 96,500 C mol−1)
Write cathode and anode reaction in a fuel cell.
Among Zn and Cu, which would occur more readily in nature as metal and which as an ion?
Define the following term:
Fuel cell
What is the SI unit tor electrochemical equivalent?
How many faradays of electricity are required for the following reaction to occur
\[\ce{MnO^-_4 -> Mn^2+}\]
Zinc can be coated on iron to produce galvanized iron but the reverse is not possible. It is because ____________.
Assertion: pure iron when heated in dry air is converted with a layer of rust.
Reason: Rust has the compositionFe3O4.
In the electrochemical cell: Zn|ZnSO4 (0.01 M)||CuSO4 (1.0 M)|Cu, the emf of this Daniel cell is E1. When the concentration of ZnSO4 is changed to 1.0 M and that CuSO4 changed to 0.01 M, the emf changes to E2. From the above, which one is the relationship between E1 and E2?
Consider the change in the oxidation state of Bromine corresponding to different emf values as shown in the diagram below:
\[\ce{BrO^-_4 ->[1.82 V] BrO^-_3 ->[1.5 V] HBrO ->[1.595 V] Br2 ->[1.0652 V] Br^-}\]
Then the species undergoing disproportionation is
A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1MY− and 1MZ− at 25°C. If the reduction potential of Z > Y > X, then ____________.
Define cathode
Describe the construction of Daniel cell. Write the cell reaction.
Why is anode in galvanic cell considered to be negative and cathode positive electrode?
Can Fe3+ oxidises bromide to bromine under standard conditions?
Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Fe^{3+}|Fe^{2+}}}}\] = 0.771 V
\[\ce{E^0_{{Br_{2}|Br^-}}}\] = −1.09 V
Is it possible to store copper sulphate in an iron vessel for a long time?
Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Cu^{2+}|{Cu}}}}\] = 0.34 V and \[\ce{E^0_{{Fe^{2+}|{Fe}}}}\] = −0.44 V
Two metals M1 and M2 have reduction potential values of −xV and +yV respectively. Which will liberate H2 and H2SO4.
For the cell \[\ce{Mg_{(s)}|Mg^{2+}_{( aq)}||Ag^+_{( aq)}|Ag_{(s)}}\], calculate the equilibrium constant at 25°C and maximum work that can be obtained during operation of cell.
Given: \[\ce{E^0_{{Mg^{2+}|Mg}}}\] = −2.37 V and \[\ce{E^0_{{Ag^{+}|Ag}}}\] = 0.80 V
Which of the following statement is correct?
Use the data given in below find out which option the order of reducing power is correct.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖`= 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-)^⊖` = 1.36 V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))^⊖` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")^⊖` = - 0.74 V
Use the data given in below find out the most stable ion in its reduced form.
`"E"_("Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)//"Cr"^(3+))^⊖`= 1.33 V `"E"_("Cl"_2//"Cl"^-)^⊖` = 1.36 V
`"E"_("MnO"_4^-//"Mn"^(2+))^⊖` = 1.51 V `"E"_("Cr"^(3+)//"Cr")^⊖` = - 0.74 V
`E_(cell)^Θ` = 1.1V for Daniel cell. Which of the following expressions are correct description of state of equilibrium in this cell?
(i) 1.1 = `K_c`
(ii) `(2.303RT)/(2F) logK_c` = 1.1
(iii) `log K_c = 2.2/0.059`
(iv) `log K_c` = 1.1
For the given cell, \[\ce{Mg | Mg^{2+} || Cu^{2+} | Cu}\]
(i) \[\ce{Mg}\] is cathode
(ii) \[\ce{Cu}\] is cathode
(iii) The cell reaction is \[\ce{Mg^+ Cu^{2+} -> Mg^{2+} + Cu}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Cu}\] is the oxidising agent
Can absolute electrode potential of an electrode be measured?
What is electrode potential?
A galvanic cell has electrical potential of 1.1V. If an opposing potential of 1.1V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
How will the pH of brine (aq. \[\ce{NaCl}\] solution) be affected when it is electrolysed?
Consider a cell given below:
\[\ce{Cu | Cu^{2+} || Cl^{-} | Cl_{2},Pt}\]
Write the reactions that occur at anode and cathode
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) K | (a) I × t |
| (ii) Λm | (b) `Λ_m/Λ_m^0` |
| (iii) α | (c) `K/c` |
| (iv) Q | (d) `G^∗/R` |
Calculate the standard EMF ofa cell which involves the following cell reactions
\[\ce{Zn + 2 Ag+ -> Zn^{2+} + 2 Ag}\]
Given that \[\ce{E^{o}_{Zn/Zn^{2+}}}\] = 0.76 volt and \[\ce{E^{o}_{Ag/Ag^{+}}}\] = – 0.80 volt.
Given the data at 25°C
Ag + I– → Agl + e–; E° = – 0.152 V
Ag → Ag+ + e–; E° = – 0.800 V
The value of log Ksp for Ag I is :-
Cell reaction is spontaneous when
The correct order of the mobility of the alkali metal ions. In aqueous solultion is
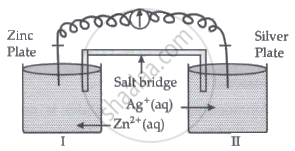
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
|
Oxidation-reduction reactions are commonly known as redox reactions. They involve transfer of electrons from one species to another. In a spontaneous reaction, energy is released which can be used to do useful work. The reaction is split into two half-reactions. Two different containers are used and a wire is used to drive the electrons from one side to the other and a Voltaic/Galvanic cell is created. It is an electrochemical cell that uses spontaneous redox reactions to generate electricity. A salt bridge also connects to the half-cells. The reading of the voltmeter gives the cell voltage or cell potential or electromotive force. If \[\ce{E^0_{cell}}\] is positive the reaction is spontaneous and if it is negative the reaction is non-spontaneous and is referred to as electrolytic cell. Electrolysis refers to the decomposition of a substance by an electric current. One mole of electric charge when passed through a cell will discharge half a mole of a divalent metal ion such as Cu2+. This was first formulated by Faraday in the form of laws of electrolysis.
|
- Is silver plate the anode or cathode? (1)
- What will happen if the salt bridge is removed? (1)
- When does electrochemical cell behaves like an electrolytic cell? (1)
- (i) What will happen to the concentration of Zn2+ and Ag+ when Ecell = 0. (1)
(ii) Why does conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution? (1)
OR
The molar conductivity of a 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2mol-1. Calculate the conductivity of this solution. (2)
On which electrode the oxidation reaction takes place?
If the value of Ksp for Hg2Cl2 (s) is X then the value of X will be ____ where pX = - log X.
Given:
\[\ce{Hg2Cl2 + 2e- -> 2Hg(l) + 2Cl-}\], E° = 0.27 V
\[\ce{Hg+2 + 2e- -> 2Hg(l)}\] E° = 0.81 V
Which of the following is incorrect?
In a solution of CuSO4, how much time will be required to precipitate 2 g copper by 0.5 ampere current?
The number of moles of electrons passed when the current of 2 A is passed through a solution of electrolyte for 20 minutes is ______.
Calculate the λ0m for Cl- ion from the data given below:
∧0m MgCl2 = 258.6 Scm2 mol-1 and λ0m Mg2+ = 106 Scm2 mol-1
The cell constant of a conductivity cell is 0.146 cm-1. What is the conductivity of 0.01 M solution of an electrolyte at 298 K, if the resistance of the cell is 1000 ohm?