Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If sec A = `sqrt2` , find : `(3cot^2 "A"+ 2 sin^2 "A")/ (tan^2 "A" – cos ^2 "A")`.
उत्तर
Consider the figure :
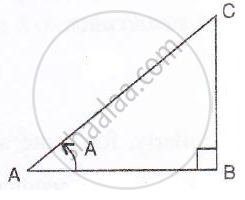
sec A = `sqrt2/1`
i.e.`"hypotenuse"/"base" = "AC"/"AB" = sqrt2/1`
Therefore if length of base = x , length of hypotenuse = `sqrt2x`
Since
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 ...[Using Pythagoras Theorem]
`(sqrt2x)^2 – (x)^2 = "BC"^2`
`"BC"^2 = 2x^2 - x^2`
BC2 = x2
∴ BC = x
Now
cos A = `1/(sec "A") = 1/(sqrt2)`
sin A = `"BC"/"AC" = 1/(sqrt2)`
tan A = `"BC"/"AB"` = 1
cot A = `1/ tan "A"` = 1
Therefore
`(3cot^2 "A"+ 2 sin^2 "A")/ (tan^2 "A" – cos ^2 "A") = (3(1)^2 + 2 (1/sqrt2)^2)/ (1^2 – ( 1/sqrt2)^2)`
= `(3 + 1)/(1– (1)/(2)`
`= 4/(1/2)`
`= 4 xx 2/1`
= 8
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If cos 2θ = sin 4θ where 2θ, 4θ are acute angles, find the value of θ.
If sin θ = ` (a^2 - b^2)/(a^2+b^2)`find all the values of all T-ratios of θ .
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that sin A = Sin B prove that ∠A = ∠B.
Evaluate:
`(sin^2 30^0 + 4 cot^2 45^0-sec^2 60^0)(cosec^2 45^0 sec^2 30^0)`
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right-angled at B and ∠A = 450. If AC = 3`sqrt(2)`cm, find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
Given : sin A = `(3)/(5)` , find : (i) tan A (ii) cos A
If tan = 0.75, find the other trigonometric ratios for A.
If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : cot2A - cosec2A
From the given figure, find all the trigonometric ratios of angle B
Evaluate: `5/(cot^2 30^circ) + 1/(sin^2 60^circ) - cot^2 45^circ + 2 sin^2 90^circ`.
