Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If sin θ = ` (a^2 - b^2)/(a^2+b^2)`find all the values of all T-ratios of θ .
उत्तर
We have sin θ = `(a^2 - b^2)/(a^2 + b^2)`
As,
`Cos^2 θ = 1 - sin^2 θ`
`= 1- ((a^2 -b^2)/(a^2 + b^2))^2`
`= 1/1 - ((a^2 - b^2)/(a^2 + b^2))^2`
`= ((a^2 + b^2)^2 -( a^2 - b^2)^2)/(a^2 + b^2)^2`
`= ([(a^2 +b^2)-(a^2-b^2)][(a^2+b^2)+(a^2-b^2)])/((a^2+b^2)^2)`
`= ([(a^2 + b^2-a^2 +b^2][a^2+b^2+a^2-b^2)])/((a^2+b^2)^2)`
`= ([2b^2][2a^2])/((a^2+b^2)^2)`
`= cos^2 θ = (4a^2b^2)/((a^2+b^2)^2)`
`= cosθ= sqrt((4a^2b^2)/(a^2+b^2)^2)`
`⟹ cos θ =(2ab)/((a^2+b^2))`
Also,
tan θ = `sinθ/cosθ`
`= (((a^2-b^2)/(a^2+b^2)))/(((2ab)/(a^2 +b^2))`
`=(a^2-b^2)/(2ab)`
Now ,
cosec θ =` 1/sinθ`
=`1/(((a^2-b^2)/(a^2-b^2)))`
`= (a^2 + b^2)/(2ab)`
Also,
sec θ`= 1/(cosθ)`
= `1/(((2ab)/(a^2+b^2)))`
= `(a^2+b^2)/(2ab)`
And,
cot θ = `1/( tan θ)`
`= 1/(((a^2-b^2)/(2ab)))`
`= (2ab)/(a^2-b^2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 3 cot A = 4, Check whether `((1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)) = cos^2 "A" - sin^2 "A"` or not.
Find acute angles A & B, if sin (A + 2B) = `sqrt3/2 cos(A + 4B) = 0, A > B`
If cot θ = `3/4` , show that `sqrt("sec θ - cosecθ"/"secθ + cosecθ" ) = 1/ sqrt(7)`
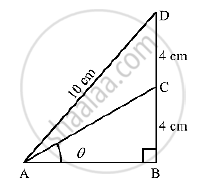
In the adjoining figure, `∠B = 90° , ∠BAC = theta° , BC = CD = 4cm and AD = 10 cm`. find (i) sin theta and (ii) `costheta`
In a ΔABC , ∠B = 90° , AB= 24 cm and BC = 7 cm find (i) sin A (ii) cos A (iii) sin C (iv) cos C
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that sin A = Sin B prove that ∠A = ∠B.
In the figure of ΔPQR , ∠P = θ° and ∠R =∅° find
(i) `sqrt(X +1) cot ∅`
(ii)`sqrt( x^3 + x ^2) tantheta`
(iii) cos θ

If 5 cos = 6 sin ; evaluate:
(i) tan θ
(ii) `(12 sin θ – 3 cos θ)/(12 sin θ + 3 cos θ)`
If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : `"cos A" + (1)/"cot A"`
Statement A (Assertion): For 0 < θ ≤ 90°, cosec θ – cot θ and cosec θ + cot θ are reciprocal of each other.
Statement R (Reason): cosec2 θ – cot2 θ = 1
