Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If 3 cot A = 4, Check whether `((1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)) = cos^2 "A" - sin^2 "A"` or not.
उत्तर १
It is given that 3cot A = 4 or cot A = `4/3`
Consider a right triangle ABC, right-angled at point B.
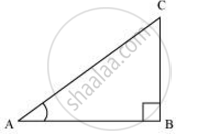
cot A =` ("Side adjacent to ∠A")/("Side opposite to ∠A")`
`("AB")/("BC") = 4/3`
If AB is 4k, then BC will be 3k, where k is a positive integer.
In ΔABC,
(AC)2 = (AB)2 + (BC)2
= (4k)2 + (3k)2
= 16k2 + 9k2
= 25k2
AC = 5k
cos A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("AB")/("AC")`
= `(4k)/(5k)`
= `4/5`
sin A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("BC")/("AC")`
= `(3k)/(5k)`
= `3/5`
tan A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("BC")/("AB")`
= `(3k)/(4k)`
= `3/4`
`(1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A) = ((1 - (3/4)^2)/(1+(3/4)^2))`
= `((1-9/16)/(1+9/16))`
= `(7/16)/(25/16)`
= `7/25`
`cos^2 A + sin^2 A = (4/5)^2 - (3/5)^2`
= `16/25 - 9/25`
= `7/25`
∴ `(1-tan^2A)/(1+tan^2 A)= cos^2A - sin^2A`
उत्तर २
3 cot A = 4, check = `(1 - tan^2 A)/(1 + tan^2 A) = cos^2 A - sin^2 A`

cot A = `"adjacent side"/"opposite side" = 4/3`
Let x be the hypotenuse
By Applying Pythagoras theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
x2 = 42 + 32
x2 = 252
x = 5
tan A = `1/(cos^2 A)` = `3/4`
cos A = `"adjacent side"/"hypotenuse" = 4/5`
sin A = `3/5`
L.H.S = `(1 - tan^2 A)/(1 + tan^2 A)`
= `(1 - (3/4)^2)/(1 + (3/4)^2)`
= `((16 - 9)/16)/((16 + 9)/16)`
= `7/25`
R.H.S cos2A - sin2 A = `(4/5)^2 - (3/5)^2`
= `(16 - 9)/25`
= `7/25`
संबंधित प्रश्न
If 𝜃 = 30° verify `cos 2 theta = (1 - tan^2 theta)/(1 + tan^2 theta)`
If A = B = 60°, verify that cos (A − B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
In right angled triangle ABC. ∠C = 90°, ∠B = 60°. AB = 15 units. Find remaining angles and sides.
If 2θ + 45° and 30° − θ are acute angles, find the degree measure of θ satisfying Sin (20 + 45°) = cos (30 - θ°)
If tan θ =`15/ 8 `, find the values of all T-ratios of θ.
If sin A = `9/41` find all the values of cos A and tan A
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that sin A = Sin B prove that ∠A = ∠B.
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that tan A= Tan B then prove that ∠A = ∠B
Evaluate:
`(sin^2 30^0 + 4 cot^2 45^0-sec^2 60^0)(cosec^2 45^0 sec^2 30^0)`
If A = 300 , verify that:
(i) sin 2A = `(2 tan A)/(1+tan^2A)`
Given: cos A = `( 5 )/ ( 13 )`
Evaluate:
- `(sin "A "–cot "A") / (2 tan "A")`
- `cot "A" + 1/cos"A"`
In the given figure;
BC = 15 cm and sin B = `(4)/(5)`
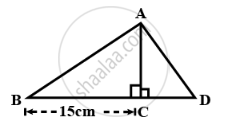
- Calculate the measure of AB and AC.
- Now, if tan ∠ADC = 1; calculate the measures of CD and AD.
Also, show that: tan2B - `1/cos^2 "B" = – 1 .`
If sin A = cos A, find the value of 2 tan2A - 2 sec2 A + 5.
If 2 sin x = `sqrt3` , evaluate.
(i) 4 sin3 x - 3 sin x.
(ii) 3 cos x - 4 cos3 x.
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
cotA = `(1)/(11)`
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
sec B = `(15)/(12)`
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°. If AB = 12units and BC = 5units, find: cot C
If sinA = 0.8, find the other trigonometric ratios for A.
If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : `"cos A" + (1)/"cot A"`
Evaluate: `5/(cot^2 30^circ) + 1/(sin^2 60^circ) - cot^2 45^circ + 2 sin^2 90^circ`.
