Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If 3 cot A = 4, Check whether `((1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A)) = cos^2 "A" - sin^2 "A"` or not.
उत्तर १
It is given that 3cot A = 4 or cot A = `4/3`
Consider a right triangle ABC, right-angled at point B.
cot A =` ("Side adjacent to ∠A")/("Side opposite to ∠A")`
`("AB")/("BC") = 4/3`
If AB is 4k, then BC will be 3k, where k is a positive integer.
In ΔABC,
(AC)2 = (AB)2 + (BC)2
= (4k)2 + (3k)2
= 16k2 + 9k2
= 25k2
AC = 5k
cos A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("AB")/("AC")`
= `(4k)/(5k)`
= `4/5`
sin A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("BC")/("AC")`
= `(3k)/(5k)`
= `3/5`
tan A = `("Side adjacent to ∠A")/"Hypotenuse" = ("BC")/("AB")`
= `(3k)/(4k)`
= `3/4`
`(1-tan^2 A)/(1+tan^2 A) = ((1 - (3/4)^2)/(1+(3/4)^2))`
= `((1-9/16)/(1+9/16))`
= `(7/16)/(25/16)`
= `7/25`
`cos^2 A + sin^2 A = (4/5)^2 - (3/5)^2`
= `16/25 - 9/25`
= `7/25`
∴ `(1-tan^2A)/(1+tan^2 A)= cos^2A - sin^2A`
उत्तर २
3 cot A = 4, check = `(1 - tan^2 A)/(1 + tan^2 A) = cos^2 A - sin^2 A`

cot A = `"adjacent side"/"opposite side" = 4/3`
Let x be the hypotenuse
By Applying Pythagoras theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
x2 = 42 + 32
x2 = 252
x = 5
tan A = `1/(cos^2 A)` = `3/4`
cos A = `"adjacent side"/"hypotenuse" = 4/5`
sin A = `3/5`
L.H.S = `(1 - tan^2 A)/(1 + tan^2 A)`
= `(1 - (3/4)^2)/(1 + (3/4)^2)`
= `((16 - 9)/16)/((16 + 9)/16)`
= `7/25`
R.H.S cos2A - sin2 A = `(4/5)^2 - (3/5)^2`
= `(16 - 9)/25`
= `7/25`
संबंधित प्रश्न
if `sec theta = 5/4` find the value of `(sin theta - 2 cos theta)/(tan theta - cot theta)`
If 8 tan A = 15, find sin A – cos A.
If ∠A and ∠P are acute angles such that tan A = tan P, then show that ∠A = ∠P.
If A and B are acute angles such that tan A = 1/2, tan B = 1/3 and tan (A + B) = `(tan A + tan B)/(1- tan A tan B)` A + B = ?
If sin 3θ = cos (θ – 6°) where 3θ and θ − 6° are acute angles, find the value of θ.
If sin θ ,` sqrt (3)/2` find the value of all T- ratios of θ .
If cos θ=0.6 show that (5sin θ -3tan θ) = 0
In a ΔABC , ∠B = 90° , AB= 24 cm and BC = 7 cm find (i) sin A (ii) cos A (iii) sin C (iv) cos C
In ΔABC , ∠C = 90° ∠ABC = θ° BC = 21 units . and AB= 29 units. Show thaT `(cos^2 theta - sin^2 theta)=41/841`
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
If A = 450, verify that :
(i) sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A
Using the formula, sin A = `sqrt((1-cos 2A)/2) ` find the value of sin 300, it being given that cos 600 = `1/2`
From the following figure, find the values of :
(i) sin A
(ii) sec A
(iii) cos2 A + sin2A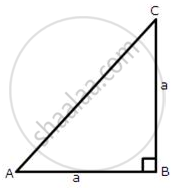
In the figure given below, ABC is an isosceles triangle with BC = 8 cm and AB = AC = 5 cm. Find:
(i) sin B
(ii) tan C
(iii) sin2 B + cos2B
(iv) tan C - cot B
In triangle ABC, ∠B = 90° and tan A = 0.75. If AC = 30 cm, find the lengths of AB and BC.
In each of the following, one trigonometric ratio is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric.
cos A = `(7)/(25)`
In ΔABC, ∠A = 90°. If AB = 5 units and AC = 12 units, find: sinB
If sinA = 0.8, find the other trigonometric ratios for A.
In an isosceles triangle ABC, AB = BC = 6 cm and ∠B = 90°. Find the values of cos C
