Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ∠A and ∠P are acute angles such that tan A = tan P, then show that ∠A = ∠P.
उत्तर
A and P are acute angle tan A = tan P
Let us consider right angled triangle ACP,
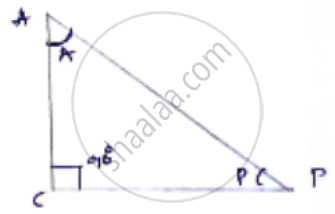
We know `tan theta = "opposite side"/"adjacent side"`
`tan A = (PC)/(AC)`
`tan P = (AC)/(PC)`
tanA =tan P ....(Given)
`(PC)/(AC) = (AC)/(PC)`
`(PC)^2 = (AC)^2`
PC = AC [∵ Angle opposite to equal sides are equal]
∠P = ∠A
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If A = 30° and B = 60°, verify that cos (A + B) = cos A cos B − sin A sin B
If sin θ ,` sqrt (3)/2` find the value of all T- ratios of θ .
If cos θ = `7/25` find the value of all T-ratios of θ .
If a right ΔABC , right-angled at B, if tan A=1 then verify that 2sin A . cos A = 1
If A = 300 , verify that:
(iii) tan 2A = `(2tanA)/(1-tan^2A)`
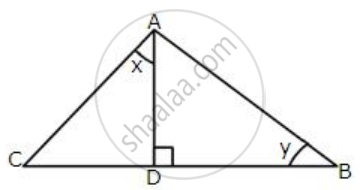
In the following figure:
AD ⊥ BC, AC = 26 CD = 10, BC = 42, ∠DAC = x and ∠B = y.
Find the value of :
(i) cot x
(ii) `1/sin^2 y – 1/tan^2 y`
(iii) `6/cos x – 5/cos y + 8 tan y`.
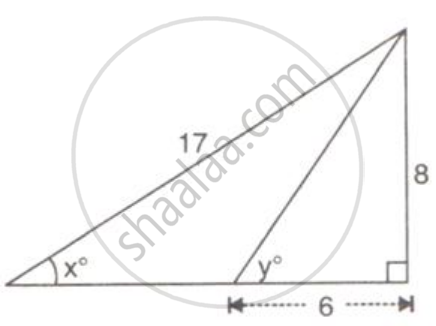
Use the given figure to find :
(i) sin xo
(ii) cos yo
(iii) 3 tan xo - 2 sin yo + 4 cos yo.
In triangle ABC, AB = AC = 15 cm and BC = 18 cm, find cos ∠ABC.
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°. If AB = 12units and BC = 5units, find: sinA
If A + B = 90°, cot B = `3/4` then tan A is equal to ______.
