Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
उत्तर १
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which CD ⊥ AB.

It is given that
cos A = cos B
⇒ `("AD")/("AC") = ("BD")/("BC")` ...(1)
We have to prove ∠A = ∠B.
To prove this, let us extend AC to P such that BC = CP.
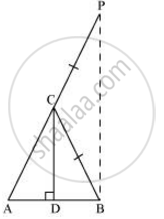
From equation (1), we obtain
`("AB")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC")`
⇒ `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("CP")` ...(By construction, we have BC = CP) ...(2)
By using the converse of B.P.T,
CD || BP
⇒ ∠ACD = ∠CPB ...(Corresponding angles) ...(3)
And, ∠BCD = ∠CBP ...(Alternate interior angles) …(4)
By construction, we have BC = CP
∴ ∠CBP = ∠CPB ...(Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle) …(5)
From equations (3), (4) and (5), we obtain
∠ACD = ∠BCD …(6)
In ΔCAD and ΔCBD,
∠ACD = ∠BCD ...[Using equation (6)]
∠CDA = ∠CDB ...[Both 90°]
Therefore, the remaining angles should be equal.
∴∠CAD = ∠CBD
⇒ ∠A = ∠B
Alternatively,
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which CD ⊥ AB.
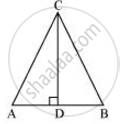
It is given that,
cos A = cos B
⇒ `("AD")/("AC") = ("BC")/("BC")`
⇒ `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC")`
Let `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC") = k`
⇒ AD = k × BD …(1)
And, AC = k × BC …(2)
Using Pythagoras theorem for triangles CAD and CBD, we obtain
CD2 = AC2 − AD2 …(3)
And, CD2 = BC2 − BD2 …(4)
From equations (3) and (4), we obtain
AC2 − AD2 = BC2 − BD2
⇒ (k BC)2 − (k BD)2 = BC2 − BD2
⇒ k2 (BC2 − BD2) = BC2 − BD2
⇒ k2 = 1
⇒ k = 1
Putting this value in equation (2), we obtain
AC = BC
⇒ ∠A = ∠B ...(Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle)
उत्तर २
∠A and ∠B are acute angles
Cos A = cos B S.T ∠A = ∠B
Let us consider right angled triangle ACB.
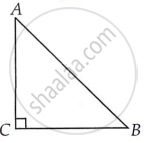
We have cos A = `"adjacent side"/"Hypotenuse"`
= `("AC")/("AB")`
cos B = `("BC")/("AB")`
cos A = cos B
`("AC")/("AB") = ("BC")/("AB")`
AC = BC
∠A = ∠B
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
cot A is the product of cot and A.
If 4 tan θ = 3, evaluate `((4sin theta - cos theta + 1)/(4sin theta + cos theta - 1))`
In the following, trigonometric ratios are given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`sin theta = sqrt3/2`
In the following, trigonometric ratios are given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`cos theta = 7/25`
In the following, one of the six trigonometric ratios is given. Find the values of the other trigonometric ratios.
`tan theta = 8/15`
If `tan theta = a/b`, find the value of `(cos theta + sin theta)/(cos theta - sin theta)`
If sec θ = `13/5, "show that" (2sinθ - 3 cosθ)/(4sinθ - 9cosθ) = 3`.
Evaluate the following
tan2 30° + tan2 60° + tan2 45°
Evaluate the following
`sin^2 30° cos^2 45 ° + 4 tan^2 30° + 1/2 sin^2 90° − 2 cos^2 90° + 1/24 cos^2 0°`
Evaluate the Following
4(sin4 30° + cos2 60°) − 3(cos2 45° − sin2 90°) − sin2 60°
`(sin theta)/(1 + cos theta)` is ______.
A ladder rests against a vertical wall at an inclination α to the horizontal. Its foot is pulled away from the wall through a distance p so that its upper end slides a distance q down the wall and then the ladder makes an angle β to the horizontal. Show that `p/q = (cos β - cos α)/(sin α - sin β)`
Prove that sec θ + tan θ = `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)`.
Proof: L.H.S. = sec θ + tan θ
= `1/square + square/square`
= `square/square` ......`(∵ sec θ = 1/square, tan θ = square/square)`
= `((1 + sin θ) square)/(cos θ square)` ......[Multiplying `square` with the numerator and denominator]
= `(1^2 - square)/(cos θ square)`
= `square/(cos θ square)`
= `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)` = R.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ sec θ + tan θ = `cos θ/(1 - sin θ)`
If sec θ = `1/2`, what will be the value of cos θ?
If f(x) = `3cos(x + (5π)/6) - 5sinx + 2`, then maximum value of f(x) is ______.
If sinθ = `1/sqrt(2)` and `π/2 < θ < π`. Then the value of `(sinθ + cosθ)/tanθ` is ______.
If cosec θ = `("p" + "q")/("p" - "q")` (p ≠ q ≠ 0), then `|cot(π/4 + θ/2)|` is equal to ______.
If θ is an acute angle and sin θ = cos θ, find the value of tan2 θ + cot2 θ – 2.
If sin θ – cos θ = 0, then find the value of sin4 θ + cos4 θ.
Evaluate: 5 cosec2 45° – 3 sin2 90° + 5 cos 0°.
