Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
उत्तर १
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which CD ⊥ AB.

It is given that
cos A = cos B
⇒ `("AD")/("AC") = ("BD")/("BC")` ...(1)
We have to prove ∠A = ∠B.
To prove this, let us extend AC to P such that BC = CP.
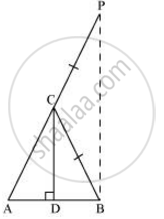
From equation (1), we obtain
`("AB")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC")`
⇒ `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("CP")` ...(By construction, we have BC = CP) ...(2)
By using the converse of B.P.T,
CD || BP
⇒ ∠ACD = ∠CPB ...(Corresponding angles) ...(3)
And, ∠BCD = ∠CBP ...(Alternate interior angles) …(4)
By construction, we have BC = CP
∴ ∠CBP = ∠CPB ...(Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle) …(5)
From equations (3), (4) and (5), we obtain
∠ACD = ∠BCD …(6)
In ΔCAD and ΔCBD,
∠ACD = ∠BCD ...[Using equation (6)]
∠CDA = ∠CDB ...[Both 90°]
Therefore, the remaining angles should be equal.
∴∠CAD = ∠CBD
⇒ ∠A = ∠B
Alternatively,
Let us consider a triangle ABC in which CD ⊥ AB.
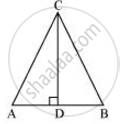
It is given that,
cos A = cos B
⇒ `("AD")/("AC") = ("BC")/("BC")`
⇒ `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC")`
Let `("AD")/("BD") = ("AC")/("BC") = k`
⇒ AD = k × BD …(1)
And, AC = k × BC …(2)
Using Pythagoras theorem for triangles CAD and CBD, we obtain
CD2 = AC2 − AD2 …(3)
And, CD2 = BC2 − BD2 …(4)
From equations (3) and (4), we obtain
AC2 − AD2 = BC2 − BD2
⇒ (k BC)2 − (k BD)2 = BC2 − BD2
⇒ k2 (BC2 − BD2) = BC2 − BD2
⇒ k2 = 1
⇒ k = 1
Putting this value in equation (2), we obtain
AC = BC
⇒ ∠A = ∠B ...(Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle)
उत्तर २
∠A and ∠B are acute angles
Cos A = cos B S.T ∠A = ∠B
Let us consider right angled triangle ACB.
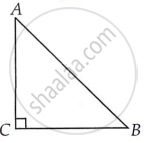
We have cos A = `"adjacent side"/"Hypotenuse"`
= `("AC")/("AB")`
cos B = `("BC")/("AB")`
cos A = cos B
`("AC")/("AB") = ("BC")/("AB")`
AC = BC
∠A = ∠B
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ΔABC right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 m. Determine:
sin C, cos C
State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
The value of tan A is always less than 1.
If `tan theta = a/b`, find the value of `(cos theta + sin theta)/(cos theta - sin theta)`
if `sec A = 17/8` verify that `(3 - 4sin^2A)/(4 cos^2 A - 3) = (3 - tan^2 A)/(1 - 3 tan^2 A)`
Evaluate the following
sin2 30° + sin2 45° + sin2 60° + sin2 90°
Evaluate the following
tan2 30° + tan2 60° + tan2 45°
Evaluate the following:
(cosec2 45° sec2 30°)(sin2 30° + 4 cot2 45° − sec2 60°)
In ΔABC is a right triangle such that ∠C = 90° ∠A = 45°, BC = 7 units find ∠B, AB and AC
If cosec θ - cot θ = `1/3`, the value of (cosec θ + cot θ) is ______.
If cos (81 + θ)° = sin`("k"/3 - theta)^circ` where θ is an acute angle, then the value of k is ______.
3 sin² 20° – 2 tan² 45° + 3 sin² 70° is equal to ______.
`(sin theta)/(1 + cos theta)` is ______.
The value of cos 0°. cos 1°. cos 2°. cos 3°… cos 89° cos 90° is ______.
If cos A = `4/5`, then the value of tan A is ______.
If 4 tanθ = 3, then `((4 sintheta - costheta)/(4sintheta + costheta))` is equal to ______.
The value of the expression (sin 80° – cos 80°) is negative.
Find the value of sin 0° + cos 0° + tan 0° + sec 0°.
If θ is an acute angle and sin θ = cos θ, find the value of tan2 θ + cot2 θ – 2.
Evaluate 2 sec2 θ + 3 cosec2 θ – 2 sin θ cos θ if θ = 45°.
In ΔBC, right angled at C, if tan A = `8/7`, then the value of cot B is ______.