Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ΔABC, D is a point in the interior of the triangle. Prove that DB + DC < AB + AC.
उत्तर

In the ΔABC,
AB + AC > BC .....(∵ Sum of the two sides of triangle is always greater than third side.) ....(i)
Also, in the ΔBDC,
BD + DC > BC ....(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii),
`"AB + AC"/"BD + DC" > "BC"/"BC"`
`"AB + AC"/"BD + DC" > 1`
AB + AC > BD + DC
i.e. BD + DC < AB + AC.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
AB and CD are respectively the smallest and longest sides of a quadrilateral ABCD (see the given figure). Show that ∠A > ∠C and ∠B > ∠D.

In the given figure, PR > PQ and PS bisects ∠QPR. Prove that ∠PSR >∠PSQ.
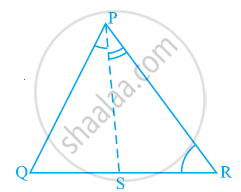
In a triangle locate a point in its interior which is equidistant from all the sides of the triangle.
In the following figure, write BC, AC, and CD in ascending order of their lengths.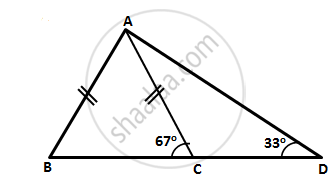
D is a point in side BC of triangle ABC. If AD > AC, show that AB > AC.
In the following figure, ∠BAC = 60o and ∠ABC = 65o.
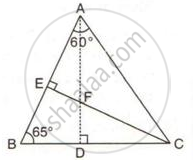
Prove that:
(i) CF > AF
(ii) DC > DF
"Caste inequalities are still prevalent in India." Examine the statement.
"Issues of caste discrimination began to be written about in many printed tracts and essays in India in the late nineteenth century." Support the statement with two suitable examples.
Name the smallest angle in each of these triangles:
In ΔXYZ, XY = 6.2cm, XY = 6.8cm and YZ = 5cm
In the given figure, T is a point on the side PR of an equilateral triangle PQR. Show that RT < QT