Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
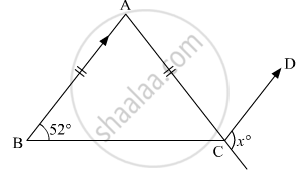
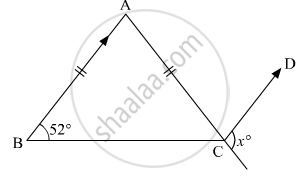
In the given figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle whose side AC is produced to E. Through C, CD is drawn parallel to BA. The value of x is
पर्याय
52°
76°
156°
104°
उत्तर
We are given that;
ΔABC , is isosceles
AB = AC
∠B = ∠C
∠C = 52
And AB || CD
We are asked to find angle x
From the figure we have
∠ACB = 52°
Therefore,
∠A = `180° - 2 xx 52° `
= 76°
Since AB || DC , so
∠ACD = ∠BAC
= 76°
Now
x + 76 = 180
= 180 - 76
= 104
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (See the given figure). Prove that
- ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
- BD = AC
- ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
Given: ZX = RP
RQ = ZY
∠PRQ = ∠XZY
So, ΔPQR ≅ ΔXYZ
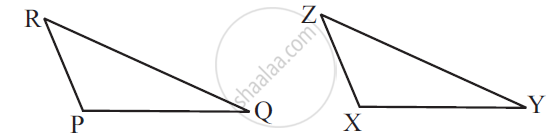
In ΔABC, ∠A = 30°, ∠B = 40° and ∠C = 110°
In ΔPQR, ∠P = 30°, ∠Q = 40° and ∠R = 110°
A student says that ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR by AAA congruence criterion. Is he justified? Why or why not?
Explain, why ΔABC ≅ ΔFED.
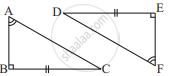
In two triangles ABC and DEF, it is given that ∠A = ∠D, ∠B = ∠E and ∠C =∠F. Are the two triangles necessarily congruent?
In the given figure, AB = DB and Ac = DC.
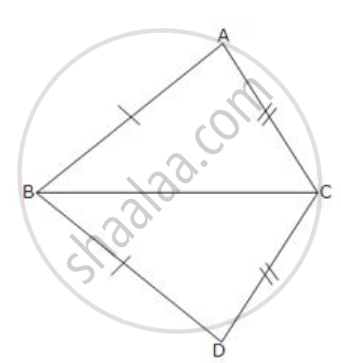
If ∠ ABD = 58o,
∠ DBC = (2x - 4)o,
∠ ACB = y + 15o and
∠ DCB = 63o ; find the values of x and y.
In the following diagram, AP and BQ are equal and parallel to each other. 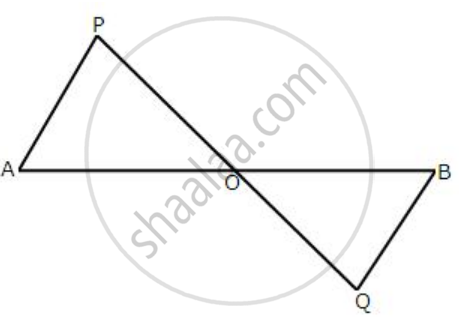
Prove that: AB and PQ bisect each other.
A point O is taken inside a rhombus ABCD such that its distance from the vertices B and D are equal. Show that AOC is a straight line.
In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC.
Prove that: ΔAOD≅ ΔCOD
In the following figure, ∠A = ∠C and AB = BC.
Prove that ΔABD ≅ ΔCBE.