Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the figure given below, find a point P on CD equidistant from points A and B.

उत्तर
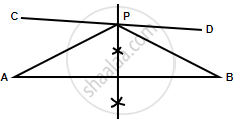
Steps of construction:
- AB and CD are the two lines given.
- Draw a perpendicular bisector of line AB which intersects CD in P.
P is the required point which is equidistant from A and B.
Since P lies on perpendicular bisector of AB; PA = PB.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Construct a right angled triangle PQR, in which ∠Q = 90°, hypotenuse PR = 8 cm and QR = 4.5 cm. Draw bisector of angle PQR and let it meets PR at point T. Prove that T is equidistant from PQ and QR.
Draw a line AB = 6 cm. Draw the locus of all the points which are equidistant from A and B.
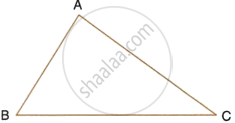
In the given triangle ABC, find a point P equidistant from AB and AC; and also equidistant from B and C.
Describe the locus of a runner, running around a circular track and always keeping a distance of 1.5 m from the inner edge.
Describe the locus of a point in rhombus ABCD, so that it is equidistant from
- AB and BC;
- B and D.
The speed of sound is 332 metres per second. A gun is fired. Describe the locus of all the people on the earth’s surface, who hear the sound exactly one second later.
A straight line AB is 8 cm long. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- always 4 cm from the line AB.
- equidistant from A and B.
Mark the two points X and Y, which are 4 cm from AB and equidistant from A and B. Describe the figure AXBY.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 6 cm, BC = 4.5 cm and AC = 5 cm. Draw and label:
- the locus of the centres of all circles which touch AB and AC,
- the locus of the centres of all the circles of radius 2 cm which touch AB.
Hence, construct the circle of radius 2 cm which touches AB and AC .
Find the locus of the centre of a circle of radius r touching externally a circle of radius R.
ΔPBC and ΔQBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base. Show that the line PQ is bisector of BC and is perpendicular to BC.
