Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 6 cm, BC = 4.5 cm and AC = 5 cm. Draw and label:
- the locus of the centres of all circles which touch AB and AC,
- the locus of the centres of all the circles of radius 2 cm which touch AB.
Hence, construct the circle of radius 2 cm which touches AB and AC .
उत्तर
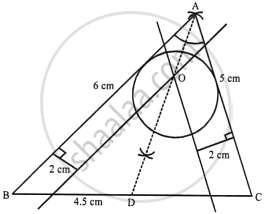
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment BC = 4.5 cm
- With B as centre and radius 6 cm and C as centre and radius 5 cm, draw arcs which intersect each other at A.
- Join AB and AC.
ABC is the required triangle. - Draw the angle bisector of ∠BAC
- Draw lines parallel to AB and AC at a distance of 2 cm, which intersect each other and AD at O.
- With centre O and radius 2 cm, draw a circle which touches AB and AC.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In each of the given figures; PA = PB and QA = QB.
| i. | 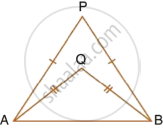 |
| ii. | 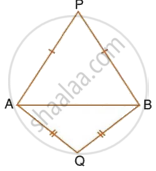 |
Prove, in each case, that PQ (produce, if required) is perpendicular bisector of AB. Hence, state the locus of the points equidistant from two given fixed points.
Construct a right angled triangle PQR, in which ∠Q = 90°, hypotenuse PR = 8 cm and QR = 4.5 cm. Draw bisector of angle PQR and let it meets PR at point T. Prove that T is equidistant from PQ and QR.
In parallelogram ABCD, side AB is greater than side BC and P is a point in AC such that PB bisects angle B. Prove that P is equidistant from AB and BC.
Use ruler and compasses only for this question.
- Construct ΔABC, where AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ABC = 60°.
- Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from BA and BC.
- Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from B and C.
- Mark the point P which is equidistant from AB, BC and also equidistant from B and C. Measure and record the length of PB.
The given figure shows a triangle ABC in which AD bisects angle BAC. EG is perpendicular bisector of side AB which intersects AD at point F.
Prove that:
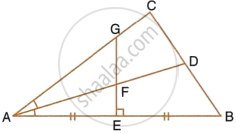
F is equidistant from A and B.
Describe the locus of points inside a circle and equidistant from two fixed points on the circumference of the circle.
Describe the locus of points at distances greater than 4 cm from a given point.
A straight line AB is 8 cm long. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- always 4 cm from the line AB.
- equidistant from A and B.
Mark the two points X and Y, which are 4 cm from AB and equidistant from A and B. Describe the figure AXBY.
In a quadrilateral PQRS, if the bisectors of ∠ SPQ and ∠ PQR meet at O, prove that O is equidistant from PS and QR.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, if the perpendicular bisectors of AB and AD meet at P, then prove that BP = DP.
