Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
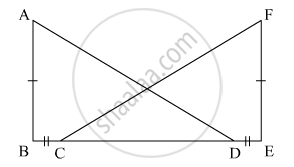
In the given figure, AB ⊥ BE and FE ⊥ BE. If BC = DE and AB = EF, then ΔABD is congruent to
पर्याय
ΔEFC
ΔECF
ΔCEF
ΔFEC
उत्तर
ΔFEC
Explanation:
It is given that
In the figure, AB ⊥ BE, FE ⊥ BE
Now, BC = DE.
Adding DC to both the sides, we get,
⇒ BC + DC = DE + DC
⇒ BD = CE
In ΔABD and ΔCEF
BD = CE (Proved)
AB = FE (Given)
∠ABD = ∠FEC (Each 90°)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔFEC by SAS congruence rule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If ΔDEF ≅ ΔBCA, write the part(s) of ΔBCA that correspond to ∠E
If ΔPQR≅ ΔEFD, then ∠E =
In the following example, a pair of triangles is shown. Equal parts of triangle in each pair are marked with the same sign. Observe the figure and state the test by which the triangles in each pair are congruent.
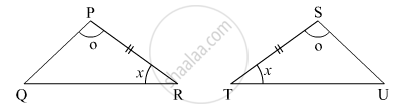
By ______ test
ΔPRQ ≅ ΔSTU
In the following diagram, AP and BQ are equal and parallel to each other.
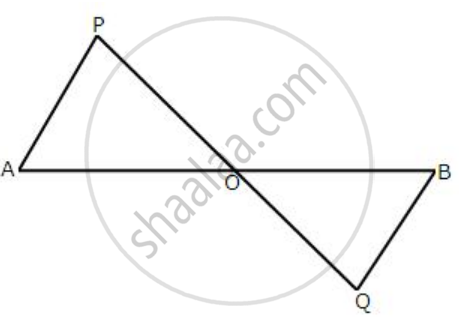
Prove that:
(i) ΔAOP≅ ΔBOQ.
(ii) AB and PQ bisect each other.
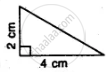
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:

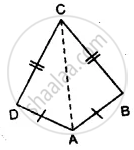
Prove that:
(i) ∆ ABC ≅ ∆ ADC
(ii) ∠B = ∠D
(iii) AC bisects angle DCB
In the figure, BC = CE and ∠1 = ∠2. Prove that ΔGCB ≅ ΔDCE.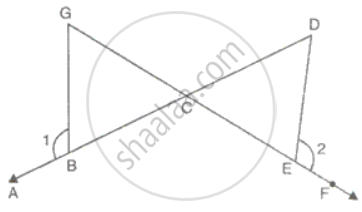
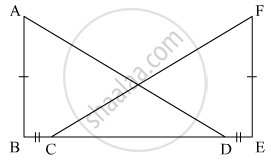
In the figure, AB = EF, BC = DE, AB and FE are perpendiculars on BE. Prove that ΔABD ≅ ΔFEC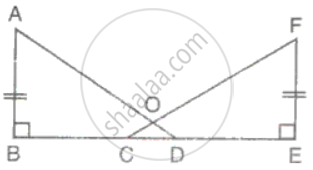
If the perpendicular bisector of the sides of a triangle PQR meet at I, then prove that the line joining from P, Q, R to I are equal.
Without drawing the triangles write all six pairs of equal measures in the following pairs of congruent triangles.
∆YZX ≅ ∆PQR
