Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, AB ⊥ BE and FE ⊥ BE. If BC = DE and AB = EF, then ΔABD is congruent to
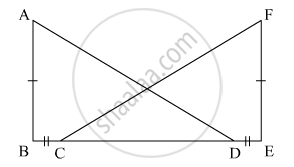
Options
ΔEFC
ΔECF
ΔCEF
ΔFEC
Solution
ΔFEC
Explanation:
It is given that
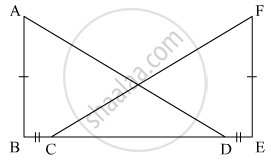
In the figure, AB ⊥ BE, FE ⊥ BE
Now, BC = DE.
Adding DC to both the sides, we get,
⇒ BC + DC = DE + DC
⇒ BD = CE
In ΔABD and ΔCEF
BD = CE (Proved)
AB = FE (Given)
∠ABD = ∠FEC (Each 90°)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔFEC by SAS congruence rule.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Prove that the sum of three altitudes of a triangle is less than the sum of its sides.
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
If ABC ≅ ΔLKM, then side of ΔLKM equal to side AC of ΔABC is
In the following figure, OA = OC and AB = BC.

Prove that: AD = CD
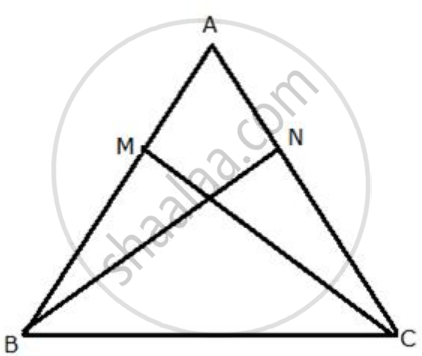
The following figure has shown a triangle ABC in which AB = AC. M is a point on AB and N is a point on AC such that BM = CN.
Prove that: (i) BN = CM (ii) ΔBMC≅ΔCNB
State, whether the pairs of triangles given in the following figures are congruent or not:
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(AB = 5cm,BC = 7cm,CA = 9cm);
ΔKLM;(KL = 7cm,LM = 5cm,KM = 9cm).
Which of the following pairs of triangles are congruent? Give reasons
ΔABC;(∠B = 70°,BC = 6cm,∠C = 50°);
ΔXYZ;(∠Z = 60°,XY = 6cm,∠X = 70°).
In ΔABC, AB = AC, BM and Cn are perpendiculars on AC and AB respectively. Prove that BM = CN.
If the given two triangles are congruent, then identify all the corresponding sides and also write the congruent angles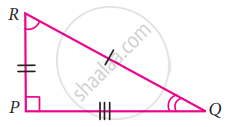

In triangles ABC and PQR, ∠A = ∠Q and ∠B = ∠R. Which side of ∆PQR should be equal to side BC of ∆ABC so that the two triangles are congruent? Give reason for your answer.
