Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
P1, P2 are points on either of the two lines `- sqrt(3) |x|` = 2 at a distance of 5 units from their point of intersection. Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendiculars drawn from P1, P2 on the bisector of the angle between the given lines.
उत्तर
Given lines are `- sqrt(3) |x|` = 2
⇒ `y - sqrt(3)x` = 2, if x ≥ 0 .....(i)
And `y + sqrt(3)x` = 2, if x < 0 ......(ii)
Slope of equation (i) is tan θ = `sqrt(3)`
∴ θ = 60°
Slope of equation (ii) is tan q `- sqrt(3)`
∴ θ = 120°
Solving equation (i) and equation (ii) we get
`y - sqrt(3) = 2`
`y + sqrt(3)x = 2`
2y = 4
⇒ y = 2
Putting the value of y is eq. (i) we get
x = 0
∴ Point of intersection of line (i) and (ii) is Q(0, 2)
∴ QO = 2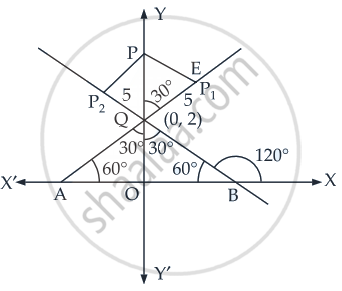
In ΔPEQ,
cos 30° = `"PQ"/"QE"`
`sqrt(3)/2 = "PQ"/5`
∴ PQ = `(5sqrt(3))/2`
∴ OP = OQ + PQ
= `2 + (5sqrt(3))/2`
Hence, the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular = `(0, 2 + (5sqrt(3))/02)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a quadrilateral in the Cartesian plane, whose vertices are (–4, 5), (0, 7), (5, –5) and (–4, –2). Also, find its area.
Without using the Pythagoras theorem, show that the points (4, 4), (3, 5) and (–1, –1) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
A line passes through (x1, y1) and (h, k). If slope of the line is m, show that k – y1 = m (h – x1).
Find the values of k for which the line (k–3) x – (4 – k2) y + k2 –7k + 6 = 0 is
- Parallel to the x-axis,
- Parallel to the y-axis,
- Passing through the origin.
Find the equation of the lines through the point (3, 2) which make an angle of 45° with the line x –2y = 3.
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis:
\[- \frac{\pi}{4}\]
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis:
\[\frac{2\pi}{3}\]
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis:
\[\frac{3\pi}{4}\]
Find the slope of the lines which make the following angle with the positive direction of x-axis: \[\frac{\pi}{3}\]
State whether the two lines in each of the following is parallel, perpendicular or neither.
Through (3, 15) and (16, 6); through (−5, 3) and (8, 2).
Find the angle between the X-axis and the line joining the points (3, −1) and (4, −2).
Line through the points (−2, 6) and (4, 8) is perpendicular to the line through the points (8, 12) and (x, 24). Find the value of x.
By using the concept of slope, show that the points (−2, −1), (4, 0), (3, 3) and (−3, 2) are the vertices of a parallelogram.
Find the equation of a straight line with slope 2 and y-intercept 3 .
Find the equation of the perpendicular to the line segment joining (4, 3) and (−1, 1) if it cuts off an intercept −3 from y-axis.
Find the equations of the straight lines which cut off an intercept 5 from the y-axis and are equally inclined to the axes.
Find the coordinates of the orthocentre of the triangle whose vertices are (−1, 3), (2, −1) and (0, 0).
The line through (h, 3) and (4, 1) intersects the line 7x − 9y − 19 = 0 at right angle. Find the value of h.
Find the angles between the following pair of straight lines:
(m2 − mn) y = (mn + n2) x + n3 and (mn + m2) y = (mn − n2) x + m3.
The medians AD and BE of a triangle with vertices A (0, b), B (0, 0) and C (a, 0) are perpendicular to each other, if
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (2, 3) on the line x + y − 11 = 0 are
The line passing through (– 2, 0) and (1, 3) makes an angle of ______ with X-axis.
If the line joining two points A(2, 0) and B(3, 1) is rotated about A in anticlock wise direction through an angle of 15°. Find the equation of the line in new position.
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point (2, 3) on the line x + y – 11 = 0 are ______.
The reflection of the point (4, – 13) about the line 5x + y + 6 = 0 is ______.
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (5, 2) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (2, 3) and (3, – 1).
Slope of a line which cuts off intercepts of equal lengths on the axes is ______.
The vertex of an equilateral triangle is (2, 3) and the equation of the opposite side is x + y = 2. Then the other two sides are y – 3 = `(2 +- sqrt(3)) (x - 2)`.
The equation of the line through the intersection of the lines 2x – 3y = 0 and 4x – 5y = 2 and
| Column C1 | Column C2 |
| (a) Through the point (2, 1) is | (i) 2x – y = 4 |
| (b) Perpendicular to the line (ii) x + y – 5 = 0 x + 2y + 1 = 0 is |
(ii) x + y – 5 = 0 |
| (c) Parallel to the line (iii) x – y –1 = 0 3x – 4y + 5 = 0 is |
(iii) x – y –1 = 0 |
| (d) Equally inclined to the axes is | (iv) 3x – 4y – 1 = 0 |
