Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
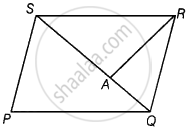
PQRS is a parallelogram whose area is 180 cm2 and A is any point on the diagonal QS. The area of ∆ASR = 90 cm2.
पर्याय
True
False
उत्तर
This statement is False.
Explanation:
Given, area of parallelogram PQRS = 180 cm2 and QS is its diagonal which divides it into two triangles of equal area.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is produced to any point P. A line through A and parallel to CP meets CB produced at Q and then parallelogram PBQR is completed (see the following figure). Show that
ar (ABCD) = ar (PBQR).
[Hint: Join AC and PQ. Now compare area (ACQ) and area (APQ)]
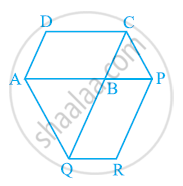
Diagonals AC and BD of a trapezium ABCD with AB || DC intersect each other at O. Prove that ar (AOD) = ar (BOC).
ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC. A line parallel to AC intersects AB at X and BC at Y. Prove that ar (ADX) = ar (ACY).
[Hint: Join CX.]
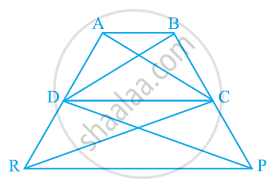
In the given figure, ar (DRC) = ar (DPC) and ar (BDP) = ar (ARC). Show that both the quadrilaterals ABCD and DCPR are trapeziums.
In the following figure, ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid-point of BC. If AE intersects BC at F, show that
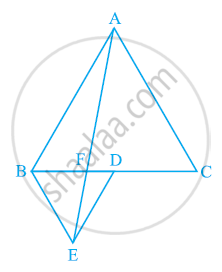
(i) ar (BDE) = 1/4 ar (ABC)
(ii) ar (BDE) = 1/2 ar (BAE)
(iii) ar (ABC) = 2 ar (BEC)
(iv) ar (BFE) = ar (AFD)
(v) ar (BFE) = 2 ar (FED)
(vi) ar (FED) = 1/8 ar (AFC)
[Hint : Join EC and AD. Show that BE || AC and DE || AB, etc.]
In the following figure, ABC is a right triangle right angled at A. BCED, ACFG and ABMN are squares on the sides BC, CA and AB respectively. Line segment AX ⊥ DE meets BC at Y. Show that:-
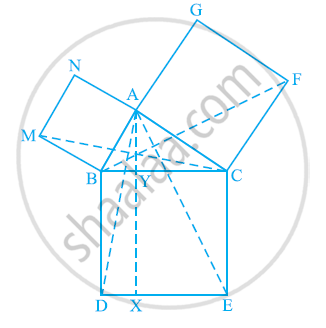
(i) ΔMBC ≅ ΔABD
(ii) ar (BYXD) = 2 ar(MBC)
(iii) ar (BYXD) = ar(ABMN)
(iv) ΔFCB ≅ ΔACE
(v) ar(CYXE) = 2 ar(FCB)
(vi) ar (CYXE) = ar(ACFG)
(vii) ar (BCED) = ar(ABMN) + ar(ACFG)
Note : Result (vii) is the famous Theorem of Pythagoras. You shall learn a simpler proof of this theorem in Class X.
In a ΔABC, if L and M are points on AB and AC respectively such that LM || BC. Prove
that:
(1) ar (ΔLCM ) = ar (ΔLBM )
(2) ar (ΔLBC) = ar (ΔMBC)
(3) ar (ΔABM) ar (ΔACL)
(4) ar (ΔLOB) ar (ΔMOC)
ABCD is a parallelogram and X is the mid-point of AB. If ar (AXCD) = 24 cm2, then ar (ABC) = 24 cm2.
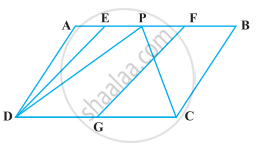
In the following figure, ABCD and EFGD are two parallelograms and G is the mid-point of CD. Then ar (DPC) = `1/2` ar (EFGD).
In ∆ABC, if L and M are the points on AB and AC, respectively such that LM || BC. Prove that ar (LOB) = ar (MOC)
