Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
Four uniform solid cubes of edges 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm are kept on the ground, touching each other in order. Locate centre of mass of their system.
उत्तर
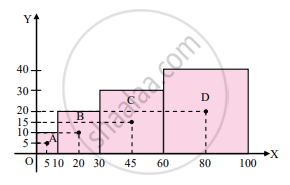
The given cubes are arranged as shown in the figure. Let one of the corners of the smallest cube lie at the origin.
As the cubes are uniform, let their center of masses lie at their respective centers.
∴ rA ≡ (5, 5), rB ≡ (20, 10), rC ≡ (45, 15) and rD ≡ (80, 20)
Also, masses of the cubes are,
`"m"_"A" = l_"A"^3 xx rho = 10^3rho`
`"m"_"B" = (20)^3 rho`
`"m"_"C" = (30)^3 rho`
`"m"_"D" = (40)^3 rho`
As the cubes are uniform, ρ is same for all of them.
∴ For X co-ordinate of centre of mass of the system,
`"X"_"cm" = (sum "m"_"i""x"_"i")/"M"`
`= ("m"_"A""x"_"A" + "m"_"B""x"_"B" + "m"_"C""x"_"C" + "m"_"D""x"_"D")/("m"_"A" + "m"_"B" + "m"_"c" + "m"_"D")`
`= ([10^3 xx rho xx 5] + [20^3 xx rho xx 20] + [30^3 xx rho xx 45] + [40^3 xx rho xx 80])/(10^3 xx rho + 20^3 xx rho + 30^3 xx rho + 40^3 xx rho)`
`= 6500/100`
= 65 cm
Similarly, Y - co-ordinate of centre of mass of system is,
`"Y"_"cm" = (sum "m"_"i""y"_"i")/"M"`
`= ("m"_"A""y"_"A" + "m"_"B""y"_"B" + "m"_"C""y"_"C" + "m"_"D""y"_"D")/("m"_"A" + "m"_"B" + "m"_"c" + "m"_"D")`
`= (10^3 xx (1 xx 5 + 8 xx 10 + 27 xx 15 + 64 xx 20))/(10^3 xx (1 + 8 + 27 + 64))`
`= 1770/100`
= 17.7 cm
Centre of mass of the system is located at point (65 cm, 17.7 cm).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10–10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
If all the particles of a system lie in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in X-Y plane?
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the noninertial character of the frame?
A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
Consider the following the equations
(A) \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\] and
(B) \[\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{\vec{F}}{M}\]
In a noninertial frame
A circular plate of diameter d is kept in contact with a square plate of edge d as show in figure. The density of the material and the thickness are same everywhere. The centre of mass of the composite system will be 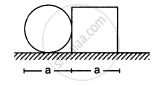
A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with the walls. The box is kept on a smooth surface. The velocity of the centre of mass
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
Seven homogeneous bricks, each of length L, are arranged as shown in figure. Each brick is displaced with respect to the one in contact by L/10. Find the x-coordinate fo the centre of mass relative to the origin shown.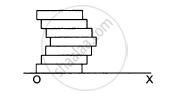
Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 30 kg are placed along a vertical line. The first block is raised through a height of 7 cm. By what distance should the second mass be moved to raise the centre of mass by 1 cm?
Two fat astronauts each of mass 120 kg are travelling in a closed spaceship moving at a speed of 15 km/s in the outer space far removed from all other material objects. The total mass of the spaceship and its contents including the astronauts is 660 kg. If the astronauts do slimming exercise and thereby reduce their masses to 90 kg each, with what velocity will the spaceship move?
A ball of mass m is dropped onto a floor from a certain height. The collision is perfectly elastic and the ball rebounds to the same height and again falls. Find the average force exerted by the ball on the floor during a long time interval.
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
A block of mass 2.0 kg moving 2.0 m/s collides head on with another block of equal mass kept at rest. (a) Find the maximum possible loss in kinetic energy due to the collision. (b) If he actual loss in kinetic energy is half of this maximum, find the coefficient of restitution.
A particle of mass 100 g moving at an initial speed u collides with another particle of same mass kept initially at rest. If the total kinetic energy becomes 0.2 J after the collision, what could be the minimum and the maximum value of u.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the block of mass m1 is pulled by a constant force F1 and the other block is pulled by a constant force F2. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
Two small balls A and B, each of mass m, are joined rigidly to the ends of a light rod of length L (see the following figure). The system translates on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity \[\nu_0\] in a direction perpendicular to the rod. A particle P of mass m kept at rest on the surface sticks to the ball A as the ball collides with it. Find
(a) the linear speeds of the balls A and B after the collision, (b) the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system A + B + P and (c) the angular speed of the system about C after the collision.
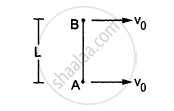
[Hint : The light rod will exert a force on the ball B
only along its length.]
Two particles P and Q of mass 1 kg and 3 kg respectively start moving towards each other from rest under mutual attraction. What is the velocity of their center of mass?
In system of two particles of masses 'm1' and 'm2', the first particle is moved by a distance 'd' towards the centre of mass. To keep the centre of mass unchanged, the second particle will have to be moved by a distance ______.
A bullet of mass 20 gram is fired from a gun of mass 2.5 kg with a speed of 750 m/s. The magnitude of recoil velocity of the gun is ______.
A shell of mass 'M' initially at rest suddenly explodes in three fragments. Two of these fragments are of mass 'M/4' each, which move with velocities 3 ms-1 and 4 ms-1 respectively in mutually perpendicular directions. The magnitude of velocity of the third fragment is ______.
Which of the following statements are correct?
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
The mass per unit length of a non-uniform rod of length L varies as m = λx where λ is constant. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
The spheres of masses 2 kg and 4 kg are situated at the opposite ends of wooden bars of length 9 m. Where does the centre of mass of the system will ______.
