Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
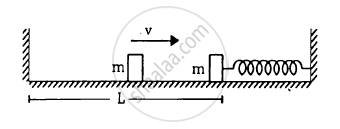
The left block in figure moves at a speed v towards the right block placed in equilibrium. All collisions to take place are elastic and the surfaces are frictionless. Show that the motions of the two blocks are periodic. Find the time period of these periodic motions. Neglect the widths of the blocks.
उत्तर
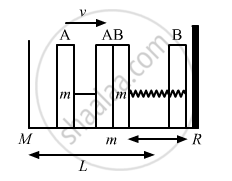
According to the question, the collision is elastic and the surface is frictionless, therefore, when the left block A moves with speed v and collides with the right block B, it transfers all the energy to the right block B.
The left block A moves a distance x against the spring; the right block returns to the original position and completes half of the oscillation.
Therefore, the period of right block B will be, \[T = \frac{2\pi\sqrt{\left( \frac{m}{k} \right)}}{2} = \pi\sqrt{\left( \frac{m}{k} \right)}\]
Right block B collides with left block A and comes to rest.
Let L be the distance moved by the block to return to its original position.
The time taken is given by,
\[\frac{L}{V} + \frac{L}{V} = 2\left( \frac{L}{V} \right)\]
Hence, time period of the periodic motion is,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
An arrow released from a bow.
Answer in brief:
Derive an expression for the period of motion of a simple pendulum. On which factors does it depend?
The length of the second’s pendulum in a clock is increased to 4 times its initial length. Calculate the number of oscillations completed by the new pendulum in one minute.
A person goes to bed at sharp 10.00 pm every day. Is it an example of periodic motion? If yes, what is the time period? If no, why?
A particle executes simple harmonic motion with a frequency v. The frequency with which the kinetic energy oscillates is
Consider a simple harmonic motion of time period T. Calculate the time taken for the displacement to change value from half the amplitude to the amplitude.
A spring stores 5 J of energy when stretched by 25 cm. It is kept vertical with the lower end fixed. A block fastened to its other end is made to undergo small oscillations. If the block makes 5 oscillations each second what is the mass of the block?
The string the spring and the pulley shown in figure are light. Find the time period of the mass m.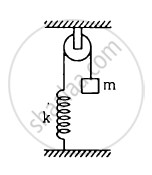
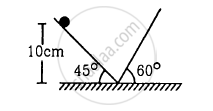
Find the time period of the motion of the particle shown in figure . Neglect the small effect of the bend near the bottom.
A uniform plate of mass M stays horizontally and symmetrically on two wheels rotating in opposite direction in Figure . The separation between the wheels is L. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plate is μ. Find the time period of oscillation of the plate if it is slightly displaced along its length and released.

The ear-ring of a lady shown in figure has a 3 cm long light suspension wire. (a) Find the time period of small oscillations if the lady is standing on the ground. (b) The lady now sits in a merry-go-round moving at 4 m/s1 in a circle of radius 2 m. Find the time period of small oscillations of the ear-ring.

Find the time period of small oscillations of the following systems. (a) A metre stick suspended through the 20 cm mark. (b) A ring of mass m and radius r suspended through a point on its periphery. (c) A uniform square plate of edge a suspended through a corner. (d) A uniform disc of mass m and radius r suspended through a point r/2 away from the centre.
A uniform disc of radius r is to be suspended through a small hole made in the disc. Find the minimum possible time period of the disc for small oscillations. What should be the distance of the hole from the centre for it to have minimum time period?
A simple pendulum is inside a spacecraft. What will be its periodic time?
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
The motion of a ball bearing inside a smooth curved bowl, when released from a point slightly above the lowermost point.
What are the two basic characteristics of a simple harmonic motion?
A person normally weighing 50 kg stands on a massless platform which oscillates up and down harmonically at a frequency of 2.0 s–1 and an amplitude 5.0 cm. A weighing machine on the platform gives the persons weight against time.
- Will there be any change in weight of the body, during the oscillation?
- If answer to part (a) is yes, what will be the maximum and minimum reading in the machine and at which position?
