Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
पर्याय
geometric structure of the molecule
mass of the molecule
the energy of the molecule
the absolute temperature of the molecule
उत्तर
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the geometric structure of the molecule.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
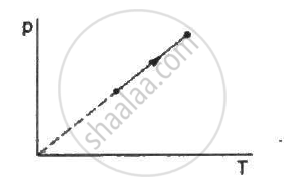
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
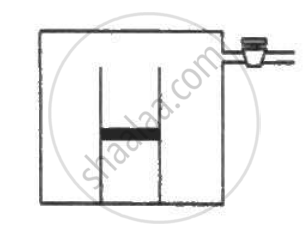
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
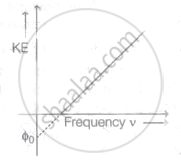
When photons of energy hv fall on a metal plate of work function 'W0', photoelectrons of maximum kinetic energy 'K' are ejected. If the frequency of the radiation is doubled, the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons will be ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
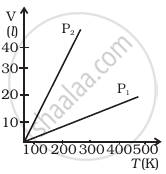
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
