Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are A (3, –1, 2), B (1, 2, –4) and C (–1, 1, 2). Find the coordinates of the fourth vertex.
उत्तर
Vertices A and C are (3, –1, 2), (−1, 1, 2) respectively.
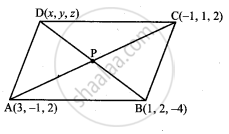
Coordinates of the midpoint P between A and C `((3 - 1)/2, (-1 + 1)/2, (2 + 2)/2)` = (1, 0, 2)
Let the coordinates of point D be (x, y, z) and the coordinates of point B be (1, 2, −4).
∴ Mid point of DB `(("x" + 1)/2, ("y" + 2)/2, ("z" - 4)/2)`
The diagonals of a parallelogram divide each other into 2 equal parts.
Therefore, `("x" + 1)/2 = 1, ("y" + 2)/2 = 0, ("z" - 4)/2 = 2`
Hence, the coordinates of point D are (1, –2, 8).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(–5, –3, –2)
Find the image of:
(–2, 3, 4) in the yz-plane.
Find the image of:
(–5, 0, 3) in the xz-plane.
Find the image of:
(–4, 0, 0) in the xy-plane.
The coordinates of a point are (3, –2, 5). Write down the coordinates of seven points such that the absolute values of their coordinates are the same as those of the coordinates of the given point.
Determine the points in zx-plane are equidistant from the points A(1, –1, 0), B(2, 1, 2) and C(3, 2, –1).
Find the point on y-axis which is equidistant from the points (3, 1, 2) and (5, 5, 2).
Find the points on z-axis which are at a distance \[\sqrt{21}\]from the point (1, 2, 3).
Show that the points A(3, 3, 3), B(0, 6, 3), C(1, 7, 7) and D(4, 4, 7) are the vertices of a square.
Find the coordinates of the point which is equidistant from the four points O(0, 0, 0), A(2, 0, 0), B(0, 3, 0) and C(0, 0, 8).
Show that the points (a, b, c), (b, c, a) and (c, a, b) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Verify the following:
(0, 7, 10), (–1, 6, 6) and (–4, 9, –6) are vertices of a right-angled triangle.
Show that the points A(1, 2, 3), B(–1, –2, –1), C(2, 3, 2) and D(4, 7, 6) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD, but not a rectangle.
Find the ratio in which the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 504 divides the line joining the points (12, –4, 8) and (27, –9, 18).
Write the distance of the point P (2, 3,5) from the xy-plane.
Write the distance of the point P(3, 4, 5) from z-axis.
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points (2, 4,5) and (3, −5, 4) is divided by the yz-plane.
Find the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points A (3, 2, 2) and B (5, 5, 4).
XOZ-plane divides the join of (2, 3, 1) and (6, 7, 1) in the ratio
What is the locus of a point for which y = 0, z = 0?
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from a point P(6,7, 8) on x - axis are
The length of the perpendicular drawn from the point P (3, 4, 5) on y-axis is
The perpendicular distance of the point P(3, 3,4) from the x-axis is
If a line makes an angle of 30°, 60°, 90° with the positive direction of x, y, z-axes, respectively, then find its direction cosines.
The x-coordinate of a point on the line joining the points Q(2, 2, 1) and R(5, 1, –2) is 4. Find its z-coordinate.
A plane meets the co-ordinates axis in A, B, C such that the centroid of the ∆ABC is the point (α, β, γ). Show that the equation of the plane is `x/alpha + y/beta + z/γ` = 3
If a line makes an angle of `pi/4` with each of y and z axis, then the angle which it makes with x-axis is ______.
Find the equation of a plane which bisects perpendicularly the line joining the points A(2, 3, 4) and B(4, 5, 8) at right angles.
Find the equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, –1) and (–1, 3, 4), and perpendicular to the plane x – 2y + 4z = 10.
The sine of the angle between the straight line `(x - 2)/3 = (y - 3)/4 = (z - 4)/5` and the plane 2x – 2y + z = 5 is ______.
The vector equation of the line through the points (3, 4, –7) and (1, –1, 6) is ______.
The angle between the line `vecr = (5hati - hatj - 4hatk) + lambda(2hati - hatj + hatk)` and the plane `vec.(3hati - 4hatj - hatk)` + 5 = 0 is `sin^-1(5/(2sqrt(91)))`.
If the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin to a plane is (5, – 3, – 2), then the equation of plane is `vecr.(5hati - 3hatj - 2hatk)` = 38.
