Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the foot of perpendicular drawn from the origin to a plane is (5, – 3, – 2), then the equation of plane is `vecr.(5hati - 3hatj - 2hatk)` = 38.
पर्याय
True
False
उत्तर
This statement is True.
Explanation:
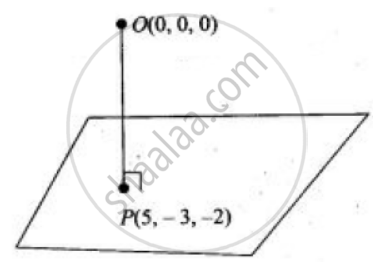
From the figure normal to the plane is `vecn = vec(OP) = 5hati - 3hatj - 2hatk`
Plane passing through the point P(5, – 3, – 2).
∴ Equation of the plane is `5(x - 5) - 3(y + 3) - 2(z + 2)` = 0
or `5x - 3y - 2z` = 38
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Coordinate planes divide the space into ______ octants.
If the origin is the centroid of the triangle PQR with vertices P (2a, 2, 6), Q (–4, 3b, –10) and R (8, 14, 2c), then find the values of a, b and c.
Name the octants in which the following points lie:
(4, –3, 5)
Find the image of:
(–5, 4, –3) in the xz-plane.
Find the image of:
(5, 2, –7) in the xy-plane.
Find the image of:
(–4, 0, 0) in the xy-plane.
A cube of side 5 has one vertex at the point (1, 0, –1), and the three edges from this vertex are, respectively, parallel to the negative x and y axes and positive z-axis. Find the coordinates of the other vertices of the cube.
Find the distances of the point P(–4, 3, 5) from the coordinate axes.
Determine the point on z-axis which is equidistant from the points (1, 5, 7) and (5, 1, –4).
Find the point on y-axis which is equidistant from the points (3, 1, 2) and (5, 5, 2).
Find the locus of P if PA2 + PB2 = 2k2, where A and B are the points (3, 4, 5) and (–1, 3, –7).
Verify the following:
(0, 7, –10), (1, 6, –6) and (4, 9, –6) are vertices of an isosceles triangle.
Verify the following:
(–1, 2, 1), (1, –2, 5), (4, –7, 8) and (2, –3, 4) are vertices of a parallelogram.
Find the locus of the points which are equidistant from the points (1, 2, 3) and (3, 2, –1).
Find the locus of the point, the sum of whose distances from the points A(4, 0, 0) and B(–4, 0, 0) is equal to 10.
Find the ratio in which the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 504 divides the line joining the points (12, –4, 8) and (27, –9, 18).
What is the locus of a point for which y = 0, z = 0?
Find the point on y-axis which is at a distance of \[\sqrt{10}\] units from the point (1, 2, 3).
Let (3, 4, –1) and (–1, 2, 3) be the end points of a diameter of a sphere. Then, the radius of the sphere is equal to
The perpendicular distance of the point P (6, 7, 8) from xy - plane is
Find the direction cosines of the line passing through the points P(2, 3, 5) and Q(–1, 2, 4).
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through (3, – 4, – 5) and (2, –3, 1) crosses the plane passing through three points (2, 2, 1), (3, 0, 1) and (4, –1, 0)
A plane meets the co-ordinates axis in A, B, C such that the centroid of the ∆ABC is the point (α, β, γ). Show that the equation of the plane is `x/alpha + y/beta + z/γ` = 3
Find the image of the point (1, 6, 3) in the line `x/1 = (y - 1)/2 = (z - 2)/3`
If a line makes an angle of `pi/4` with each of y and z axis, then the angle which it makes with x-axis is ______.
Find the equation of the plane which is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y + 6z + 8 = 0 and which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z – 4 = 0 and 2x + y – z + 5 = 0.
If the directions cosines of a line are k, k, k, then ______.
The sine of the angle between the straight line `(x - 2)/3 = (y - 3)/4 = (z - 4)/5` and the plane 2x – 2y + z = 5 is ______.
