Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two submarines are approaching each other in a calm sea. The first submarine travels at a speed of 36 km h−1 and the other at 54 km h−1 relative to the water. The first submarine sends a sound signal (sound waves in water are also called sonar) at a frequency of 2000 Hz. (a) At what frequency is this signal received from the second submarine. At what frequency is this signal received by the first submarine. Take the speed of of the sound wave in water to be 1500 m s−1.
उत्तर
Given:
Velocity of water v = 1500 m/s
Frequency of sound signal \[f_0\]= 2000 Hz
Velocity of first submarine vs = 36 kmh−1 = \[36 \times \frac{5}{18} \text{ m/s }\]
Velocity of second submarine \[v_0\]= 54 km h−1 = \[54 \times \frac{5}{18}\] m/s = 15 m/s
Frequency received by the first submarine \[\left( f_1 \right)\] is given by:
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{v + v_0}{v - v_s} \right) f_0\]
On substituting the values, we get:
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{1500 + 15}{1500 - 10} \right) \times (2000)\]
\[ = 2034 \text { Hz }\]
(b) Here,
\[f_0 = 2034 Hz\]
Apparent frequency received by second submarine \[\left( f_2 \right)\] is given by :
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{1500 + 10}{1500 - 15} \right) \times (2034)\]
\[ = 2068 \text { Hz }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following is a mechanical wave?
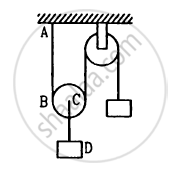
Both the strings, shown in figure, are made of same material and have same cross section. The pulleys are light. The wave speed of a transverse wave in the string AB is
\[\nu_1\] and in CD it is \[\nu_2\]. Then \[\nu_1 / \nu_2\]
Two periodic waves of amplitudes A1 and A2 pass thorough a region. If A1 > A2, the difference in the maximum and minimum resultant amplitude possible is
The fundamental frequency of a string is proportional to
following Figure shows a wave pulse at t = 0. The pulse moves to the right with a speed of 10 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 1 s, 2 s and 3 s.
At a prayer meeting, the disciples sing JAI-RAM JAI-RAM. The sound amplified by a loudspeaker comes back after reflection from a building at a distance of 80 m from the meeting. What maximum time interval can be kept between one JAI-RAM and the next JAI-RAM so that the echo does not disturb a listener sitting in the meeting. Speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
The speed of sound as measured by a student in the laboratory on a winter day is 340 m s−1 when the room temperature is C17°. What speed will be measured by another student repeating the experiment on a day when the room temperature is 32°C?
A one-metre long stretched string having a mass of 40 g is attached to a tuning fork. The fork vibrates at 128 Hz in a direction perpendicular to the string. What should be the tension in the string if it is to vibrate in four loops?
Find the fundamental, first overtone and second overtone frequencies of an open organ pipe of length 20 cm. Speed of sound in air is 340 ms−1.
An open organ pipe has a length of 5 cm. (a) Find the fundamental frequency of vibration of this pipe. (b) What is the highest harmonic of such a tube that is in the audible range? Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the audible range is 20-20,000 Hz.
An electronically driven loudspeaker is placed near the open end of a resonance column apparatus. The length of air column in the tube is 80 cm. The frequency of the loudspeaker can be varied between 20 Hz and 2 kHz. Find the frequencies at which the column will resonate. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A piston is fitted in a cylindrical tube of small cross section with the other end of the tube open. The tube resonates with a tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz. The piston is gradually pulled out of the tube and it is found that a second resonance occurs when the piston is pulled out through a distance of 32.0 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in the air of the tube.
Calculate the frequency of beats produced in air when two sources of sound are activated, one emitting a wavelength of 32 cm and the other of 32.2 cm. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1.
Two identical tuning forks vibrating at the same frequency 256 Hz are kept fixed at some distance apart. A listener runs between the forks at a speed of 3.0m s−1 so that he approaches one tuning fork and recedes from the other figure. Find the beat frequency observed by the listener. Speed of sound in air = 332 m s−1.
A car moving at 108 km h−1 finds another car in front it going in the same direction at 72 km h−1. The first car sounds a horn that has a dominant frequency of 800 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency heard by the driver in the front car? Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A wave of frequency 500 Hz is traveling with a speed of 350 m/s. (a) What is the phase difference between two displacements at a certain point at times 1.0 ms apart? (b) what will be the smallest distance between two points which are 45° out of phase at an instant of time?
The speed of sound in hydrogen is 1270 m/s. The speed of sound in the mixture of oxygen and hydrogen in which they are mixed in 1:4 ratio is
Change in temperature of the medium changes ______.
A spring breaks under tension of 10 kg wt.If the string is used to revolve a body of mass 1.2 kg in a horizontal circle. of radius 50 cm, what is the maximum speed with which a body can be revolved?
