Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
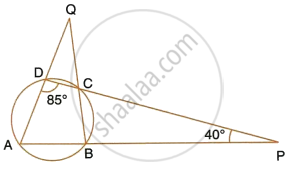
Use the given figure to find:
- ∠BAD,
- ∠DQB.
उत्तर
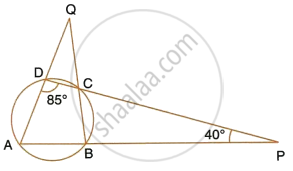
i. By angle sum property of ∆ADP,
∠BAD = 180° – 85° – 40° = 55°
ii. ∠ABC = 180° – ∠ADC = 180° – 85° = 95°
(Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
By angle sum property,
∠AQB = 180° – 95° – 55°
`=>` ∠DQB = 30°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which BC is parallel to AD, angle ADC = 110° and angle BAC = 50°. Find angle DAC and angle DCA.
In a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A : ∠C = 3 : 1 and ∠B : ∠D = 1 : 5; find each angle of the quadrilateral.
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. The tangents at B and D intersect each other at point P. If AB is parallel to CD and ∠ABC = 55°, find:
- ∠BOD
- ∠BPD
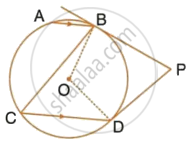
The bisectors of the opposite angles A and C of a cydic quadrilateral ABCD intersect the cirde at the points E and F, respectively. Prove that EF is a diameter of the circle.
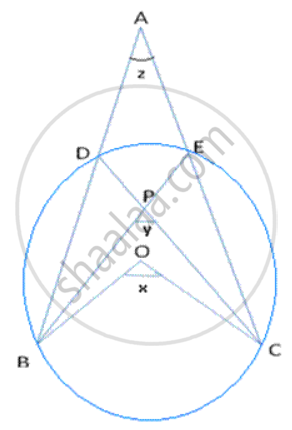
In following fig., O is the centre of the circle, prove that ∠x =∠ y + ∠ z.
In the following figure, O is the centre of the circle. Find the values of a, b and c.
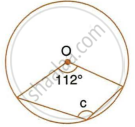
In the figure, given below, find: ∠ABC. Show steps of your working.

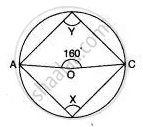
In the given below the figure, O is the centre of the circle and ∠ AOC = 160°. Prove that 3∠y - 2∠x = 140°.
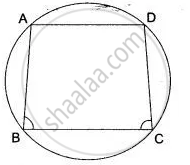
If ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AD || BC. Prove that ∠B = ∠C.
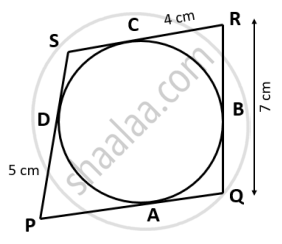
In the given figure, the sides of the quadrilateral PQRS touches the circle at A, B, C and D. If RC = 4 cm, RQ = 7 cm and PD = 5 cm. Find the length of PQ: