Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
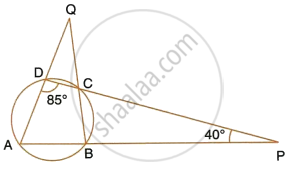
Use the given figure to find:
- ∠BAD,
- ∠DQB.
Solution
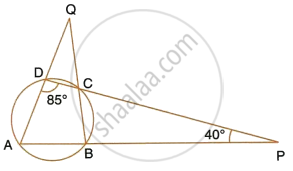
i. By angle sum property of ∆ADP,
∠BAD = 180° – 85° – 40° = 55°
ii. ∠ABC = 180° – ∠ADC = 180° – 85° = 95°
(Pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
By angle sum property,
∠AQB = 180° – 95° – 55°
`=>` ∠DQB = 30°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the figure given, O is the centre of the circle. ∠DAE = 70°. Find giving suitable reasons, the measure of:
- ∠BCD
- ∠BOD
- ∠OBD
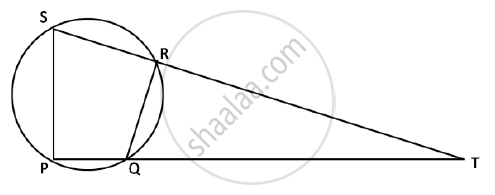
In the given figure PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral PQ and SR produced meet at T
1) Prove ΔTPS ~ ΔTRQ.
2) Find SP if TP = 18 cm, RQ = 4 cm and TR = 6 cm
3) Find the area of quadrilateral PQRS if the area of ΔPTS = 27 cm2.
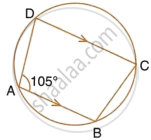
In the figure, given below, find:
- ∠BCD,
- ∠ADC,
- ∠ABC.
Show steps of your working.
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AB and DC on being produced, meet at P such that PA = PD. Prove that AD is parallel to BC.
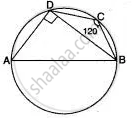
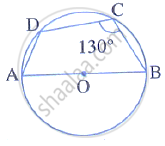
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of a circle with centre O. ∠BCD = 130°. Find:
(i) ∠DAB
(ii) ∠DBA
In the following figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AD is parallel to BC.
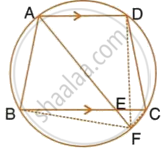
If the bisector of angle A meets BC at point E and the given circle at point F, prove that:
- EF = FC
- BF = DF
In following figure.,ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral . If ∠ BCD = 100° and ∠ ABD = 70° , find ∠ ADB.
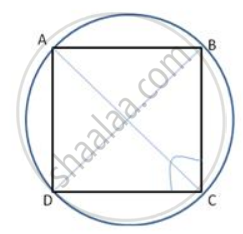
The diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral are at right angles. Prove that the perpendicular from the point of their intersection on any side when produced backward bisects the opposite side.
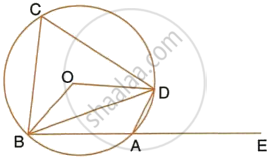
In Fig. ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. A circle passing through A and B meets AD and BC in the points E and F respectively. Prove that EF || DC.
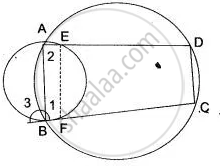
In the adjoining figure, AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O. If ∠BCD = 120°, calculate:
(i) ∠BAD (ii) ∠DBA