Advertisements
Advertisements
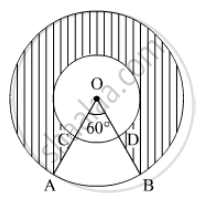
In Figure , two concentric circles with centre O, have radii 21cm and 42 cm. If ∠ AOB = 60°, find the area of the shaded region. [use π=22/7]
Concept: Circumference of a Circle
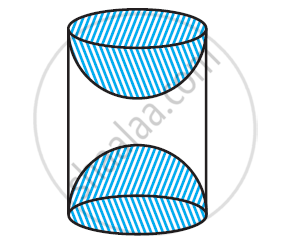
A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder, as shown in given figure. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the total surface area of the article.
[Use `pi = 22/7`]
Concept: Surface Area of a Combination of Solids
Prove that `sqrt3` is an irrational number.
Concept: Proofs of Irrationality
If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial x2 – 1, then the value of (α + β) is ______.
Concept: Geometrical Meaning of the Zeroes of a Polynomial
Solve the following quadratic equation for x: `4x^2 + 4bx – (a^2 – b^2) = 0`
Concept: Solutions of Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
Find the value of p, for which one root of the quadratic equation px2 – 14x + 8 = 0 is 6 times the other.
Concept: Nature of Roots of a Quadratic Equation
In an AP of 50 terms, the sum of first 10 terms is 210 and the sum of its last 15 terms is 2565. Find the A.P.
Concept: Arithmetic Progression
Find the ratio in which y-axis divides the line segment joining the points A(5, –6) and B(–1, –4). Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Concept: Section Formula
Assertion (A): The point (0, 4) lies on y-axis.
Reason (R): The x-coordinate of a point on y-axis is zero.
Concept: Coordinate Geometry
Assertion (A): The point (0, 4) lies on y-axis.
Reason (R): The x-coordinate of a point on y-axis is zero.
Concept: Coordinate Geometry
In the following figure, altitudes AD and CE of ΔABC intersect each other at the point P. Show that:
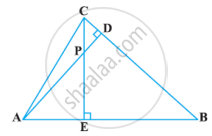
ΔABD ∼ ΔCBE
Concept: Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
Sides AB and AC and median AD of a triangle ABC are respectively proportional to sides PQ and PR and median PM of another triangle PQR. Show that ΔABC ~ ΔPQR.
Concept: Criteria for Similarity of Triangles
Construct a triangle ABC with sides BC = 7 cm, ∠B = 45° and ∠A = 105°. Then construct a triangle whose sides are `3/4` times the corresponding sides of ∆ABC.
Concept: Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Acute Angle and Obtuse Angle
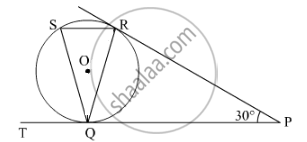
In the given figure, tangents PQ and PR are drawn from an external point P to a circle with centre O, such that ∠RPQ = 30°. A chord RS is drawn parallel to the tangent PQ. Find ∠RQS.
Concept: Concept of Circle
Two concentric circles are of radii 5 cm and 3 cm. Find the length of the chord of the larger circle which touches the smaller circle.
Concept: Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle
In the given figure, XY and X’Y’ are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X’Y’ at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90°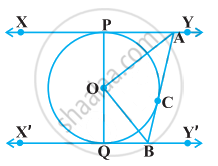
Concept: Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle
A circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral ABCD. Prove that AB + CD = BC + DA.
Concept: Tangent to a Circle
If a circle is touching the side BC of ΔABC at P and is touching AB and AC produced at Q and R respectively (see the figure). Prove that AQ = `1/2` (perimeter of ΔABC).
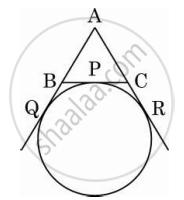
Concept: Number of Tangents from a Point on a Circle
Prove that `tan θ/(1 - cot θ) + cot θ/(1 - tanθ)` = 1 + sec θ cosec θ
Concept: Trigonometric Ratios
From the top of a 7 m high building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower is 60° and the angle of depression of its foot is 45°. Determine the height of the tower.
Concept: Heights and Distances
