Advertisements
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 - Oscillations Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 - Oscillations - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Oscillations
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 10 Oscillations Evaluation [Pages 218 - 221]
Multiple Choice Questions
In a simple harmonic oscillation, the acceleration against displacement for one complete oscillation will be __________.
an ellipse
a circle
a parabola
a straight line
A particle executing SHM crosses points A and B with the same velocity. Having taken 3 s in passing from A to B, it returns to B after another 3 s. The time period is ____________.
15 s
6 s
12 s
9 s
The length of a second’s pendulum on the surface of the Earth is 0.9 m. The length of the same pendulum on the surface of planet X such that the acceleration of the planet X is n times greater than the Earth is
0.9 n
`0.9/"n""m"`
0.9 n2m
`0.9/"n"^2`
A simple pendulum is suspended from the roof of a school bus which moves in a horizontal direction with an acceleration a, then the time period is
`"T" ∝ 1/("g"^2 + "a"^2)`
`"T" ∝ 1/sqrt("g"^2 + "a"^2)`
`"T" ∝ sqrt("g"^2 + "a"^2)`
`"T" ∝ ("g"^2 + "a"^2)`
Two bodies A and B whose masses are in the ratio 1 : 2 are suspended from two separate massless springs of force constants kA and kB respectively. If the two bodies oscillate vertically such that their maximum velocities are in the ratio 1 : 2, the ratio of the amplitude A to that of B is
`sqrt(("k"_"B")/(2"k"_"A"))`
`sqrt(("k"_"B")/(8"k"_"A"))`
`sqrt((2"k"_"B")/("k"_"A"))`
`sqrt((8"k"_"B")/("k"_"A"))`
A spring is connected to a mass m suspended from it and its time period for vertical oscillation is T. The spring is now cut into two equal halves and the same mass is suspended from one of the halves. The period of vertical oscillation is
T’ = `sqrt2"T"`
T’ = `"T"/sqrt2`
T’ = `sqrt(2"T")`
T’ = `sqrt("T"/2)`
The time period for small vertical oscillations of block of mass m when the masses of the pulleys are negligible and spring constant k1 and k2 is
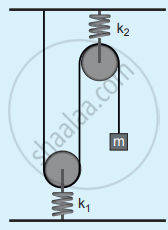
T = `4π sqrt("m"(1/"k"_1 + 1/"k"_2))`
T = `2π sqrt("m"(1/"k"_1 + 1/"k"_2))`
T = `4π sqrt("m"("k"_1 + "k"_2))`
T = `2π sqrt("m"("k"_1 + "k"_2))`
A simple pendulum has a time period T1. When its point of suspension is moved vertically upwards according to as y = kt2, where y is the vertical distance covered and k = 1 ms−2, its time period becomes T2. Then, T `"T"_1^2/"T"_2^2` is (g = 10 ms−2)
`5/6`
`11/10`
`6/5`
`5/4`
An ideal spring of spring constant k, is suspended from the ceiling of a room and a block of mass M is fastened to its lower end. If the block is released when the spring is un-stretched, then the maximum extension in the spring is
`4"Mg"/"k"`
`"Mg"/"k"`
`2"Mg"/"k"`
`"Mg"/(2"k")`
A pendulum is hung in a very high building oscillates to and fro motion freely like a simple harmonic oscillator. If the acceleration of the bob is 16 ms−2 at a distance of 4 m from the mean position, then the time period is
2 s
1 s
2πs
πs
A hollow sphere is filled with water. It is hung by a long thread. As the water flows out of a hole at the bottom, the period of oscillation will ____________.
first increase and then decrease
first decrease and then increase
increase continuously
decrease continuously
The damping force on an oscillator is directly proportional to the velocity. The units of the constant of proportionality are
kg ms−1
kg ms−2
kg s−1
kg s
When a damped harmonic oscillator completes 100 oscillations, its amplitude is reduced to `1/3` of its initial value. What will be its amplitude when it completes 200 oscillations?
`1/5`
`2/3`
`1/6`
`1/9`
Which of the following differential equations represents a damped harmonic oscillator?
`("d"^2"y")/"dt"^2 + "y" = 0`
`("d"^2"y")/"dt"^2 + γ"dy"/"dt" + "y" = 0`
`("d"^2"y")/"dt"^2 + "k"^2"y" = 0`
`"dy"/"dt" + "y" = 0`
If the inertial mass and gravitational mass of the simple pendulum of length l are not equal, then the time period of the simple pendulum is
T = `2π sqrt(("m"_"i""l")/("m"_"g""g"))`
T = `2π sqrt(("m"_"g""l")/("m"_"i""g"))`
T = `2π "m"_"g"/"m"_"i" sqrt("l"/"g")`
T = `2π "m"_"i"/"m"_"g" sqrt("l"/"g")`
Short Answers Questions
What is meant by periodic motion? Give any two examples, for periodic motion.
What is meant by non-periodic motion? Give any two examples, for non-periodic motion.
What is meant by the force constant of a spring?
Define the time period of simple harmonic motion.
Define the frequency of simple harmonic motion.
What is an epoch?
Write short notes on two springs connected in series.
Write short notes on two springs connected in parallel.
Write down the time period of simple pendulum.
State the laws of the simple pendulum?
Write down the equation of the time period for the linear harmonic oscillator.
What is meant by free oscillation?
Explain damped oscillation. Give an example.
Define forced oscillation. Give an example.
What is meant by maintained oscillation? Give an example.
Explain resonance. Give an example.
Long Answers Questions
What is meant by simple harmonic oscillation? Give examples and explain why every simple harmonic motion is a periodic motion whereas the converse need not be true.
Describe Simple Harmonic Motion as a projection of uniform circular motion.
What is meant by angular harmonic oscillation? Compute the time period of angular harmonic oscillation.
Write down the difference between simple harmonic motion and angular simple harmonic motion.
Discuss the simple pendulum in detail.
Explain the horizontal oscillations of a spring.
Describe the vertical oscillations of a spring.
Write short notes on the oscillations of the liquid column in the U-tube.
Discuss in detail the energy in simple harmonic motion.
Explain in detail the four different types of oscillations.
Numerical Problems
Consider the Earth as a homogeneous sphere of radius R and a straight hole is bored in it through its centre. Show that a particle dropped into the hole will execute a simple harmonic motion such that its time period is
T = `2π sqrt("R"/"g")`
Consider a simple pendulum of length l = 0.9 m which is properly placed on a trolley rolling down on a inclined plane which is at θ = 45° with the horizontal. Assuming that the inclined plane is frictionless, calculate the time period of oscillation of the simple pendulum.
A piece of wood of mass m is floating erect in a liquid whose density is ρ. If it is slightly pressed down and released, then executes simple harmonic motion. Show that its time period of oscillation is T = `2π sqrt("m"/("Ag"ρ))`
Consider two simple harmonic motion along the x and y-axis having the same frequencies but different amplitudes as x = A sin (ωt + φ) (along x-axis) and y = B sin ωt (along y-axis). Then show that
`"x"^2/"A"^2 + "y"^2/"B"^2 - (2"xy")/"AB" cos φ = sin^2 φ`
and also discuss the special cases when
- φ = 0
- φ = π
- φ = `π/2`
- φ = `π/2` and A = B
- φ = `π/4`
Note: when a particle is subjected to two simple harmonic motions at right angle to each other the particle may move along different paths. Such paths are called Lissajous figures.
Show that for a particle executing simple harmonic motion.
- the average value of kinetic energy is equal to the average value of potential energy.
- average potential energy = average kinetic energy = `1/2` (total energy)
Hint: average kinetic energy = <kinetic energy> = `1/"T" int_0^"T" ("Kinetic energy") "dt"` and
average potential energy = <potential energy> = `1/"T" int_0^"T" ("Potential energy") "dt"`
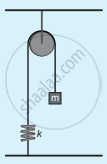
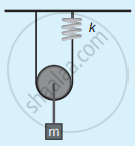
Compute the time period for the following system if the block of mass m is slightly displaced vertically down from its equilibrium position and then released. Assume that the pulley is light and smooth, strings and springs are light.
Solutions for 10: Oscillations
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 - Oscillations Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 - Oscillations - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 - Oscillations
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 10 (Oscillations) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 10 Oscillations are Oscillations, Simple Harmonic Motion (S.H.M.), Angular Simple Harmonic Motion, Linear Simple Harmonic Oscillator, Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion, Types of Oscillations.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Oscillations exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Oscillations Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
