Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ball is thrown horizontally from a point 100 m above the ground with a speed of 20 m/s. Find the velocity (direction and magnitude) with which it strikes the ground.
Solution
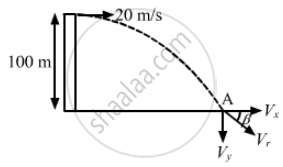
Given:
Speed of the ball, ux = 20 m/s
Height from which the ball is dropped, h = 100 m
We know that horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion of the ball.
At A, vx = 20 m/s.
vy = u + gt = 0 + 9.8 × 4.5
⇒vy = 44.1 m/s
Resultant velocity:
\[v_r = \sqrt{\left( 44 . 1 \right)^2 + \left( 20 \right)^2} \approx 49 \text{ m } /s\]
\[\tan \beta = \frac{v_y}{v_x} = \frac{44 . 1}{20} = 2 . 205\]
\[ \Rightarrow \beta = \tan^{- 1} \left( 2 . 205 \right) = 66^\circ \]
Therefore, the ball strikes the ground with a magnitude of velocity 49 m/s and the direction at an angle of 66° with the ground.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 m s–1.
- What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball?
- What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point of its motion?
- Choose the x = 0 m and t = 0 s to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically downward direction to be the positive direction of x-axis, and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion.
- To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hands? (Take g = 9.8 m s–2 and neglect air resistance).
A boy standing on a stationary lift (open from above) throws a ball upwards with the maximum initial speed he can, equal to 49 m/s. How much time does the ball take to return to his hands? If the lift starts moving up with a uniform speed of 5 m/s and the boy again throws the ball up with the maximum speed he can, how long does the ball take to return to his hands?
Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff 200 m high with initial speeds of 15 m/s and 30 m/s. Verify that the graph shown in Fig. 3.27 correctly represents the time variation of the relative position of the second stone with respect to the first. Neglect air resistance and assume that the stones do not rebound after hitting the ground. Take g = 10 m/s2. Give the equations for the linear and curved parts of the plot.
At which point on its path a projectile has the smallest speed?
In a projectile motion the velocity
Two bullets are fired simultaneously, horizontally and with different speeds from the same place. Which bullet will hit he ground first?
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the total distance moved by the train .
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the time to reach the maximum height .
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 28 m/s.Find its velocity one second before it reaches the maximum height.
A ball is thrown horizontally from a point 100 m above the ground with a speed of 20 m/s. Find the time it takes to reach the ground .
A ball is thrown at a speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Find the maximum height reached .
In a soccer practice session the football is kept at the centre of the filed 40 yards from the 10 ft high goalposts. A goal is attempted by kicking the football at a speed of 64 ft/s at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. Will the ball reach the goal post?
A popular game in Indian villages is goli which is played with small glass balls called golis. The goli of one player is situated at a distance of 2.0 m from the goli of the second player. This second player has to project his goli by keeping the thumb of the left hand at the place of his goli, holding the goli between his two middle fingers and making the throw. If the projected goli hits the goli of the first player, the second player wins. If the height from which the goli is projected is 19.6 cm from the ground and the goli is to be projected horizontally, with what speed should it be projected so that it directly hits the stationery goli without falling on the ground earlier?
A bomb is dropped from a plane flying horizontally with uniform speed. Show that the bomb will explode vertically below the plane. Is the statement true if the plane flies with uniform speed but not horizontally?
A boy standing on a long railroad car throws a ball straight upwards. The car is moving on the horizontal road with an acceleration of 1 m/s2 and the projection velocity in the vertical direction is 9.8 m/s. How far behind the boy will the ball fall on the car?
The benches of a gallery in a cricket stadium are 1 m wide and 1 m high. A batsman strikes the ball at a level one metre above the ground and hits a mammoth sixer. The ball starts at 35 m/s at an angle of 53° with the horizontal. The benches are perpendicular to the plane of motion and the first bench is 110 m from the batsman. On which bench will the ball hit?
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. If he heads in a direction making an angle θ with the flow, find the time he takes to cross the river.
Two friends A and B are standing a distance x apart in an open field and wind is blowing from A to B. A beat a drum and B hears the sound t1 time after he sees the event. A and B interchange their positions and the experiment is repeated. This time B hears the drum timer after he sees the event. Calculate the velocity of sound in still air v and the velocity of wind u. Neglect the time light takes in travelling between the friends.
A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and other after a time interval (less than 2 seconds). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the first. The vertical gap between first and second ball is +15 m at t = 2 s. The gap is found to remain constant. Calculate the velocity with which the balls were thrown and the exact time interval between their throw.
