Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. A particular particle has zero displacement at a certain instant. The particle closest to it having zero displacement is at a distance
Options
\[\lambda/4\]
\[\lambda/3\]
\[\lambda/2\]
\[\lambda\]
Solution
\[\lambda/2\]
A sine wave has a maxima and a minima and the particle displacement has phase difference of π radians. Therefore, applying similar argument we can say that if a particular particle has zero displacement at a certain instant, then the particle closest to it having zero displacement is at a distance is equal to
\[\lambda/2\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You have learnt that a travelling wave in one dimension is represented by a function y= f (x, t)where x and t must appear in the combination x – v t or x + v t, i.e. y = f (x ± v t). Is the converse true? Examine if the following functions for y can possibly represent a travelling wave:
(a) `(x – vt )^2`
(b) `log [(x + vt)/x_0]`
(c) `1/(x + vt)`
(i) For the wave on a string described in Exercise 15.11, do all the points on the string oscillate with the same (a) frequency, (b) phase, (c) amplitude? Explain your answers. (ii) What is the amplitude of a point 0.375 m away from one end?
A train, standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. (i) What is the frequency of the whistle for a platform observer when the train (a) approaches the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1, (b) recedes from the platform with a speed of 10 m s–1? (ii) What is the speed of sound in each case? The speed of sound in still air can be taken as 340 m s–1.
A SONAR system fixed in a submarine operates at a frequency 40.0 kHz. An enemy submarine moves towards the SONAR with a speed of 360 km h–1. What is the frequency of sound reflected by the submarine? Take the speed of sound in water to be 1450 m s–1.
Show that for a wave travelling on a string
\[\frac{y_{max}}{\nu_{max}} = \frac{\nu_{max}}{\alpha_{max}},\]
where the symbols have usual meanings. Can we use componendo and dividendo taught in algebra to write
\[\frac{y_{max} + \nu_{max}}{\nu_{max} - \nu_{max}} = \frac{\nu_{max} + \alpha_{max}}{\nu_{max} - \alpha_{max}}?\]
Two sine waves travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of each wave is A and the phase difference between the two waves is 120°. The resultant amplitude will be
A sonometer wire supports a 4 kg load and vibrates in fundamental mode with a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. The length of the wire between the bridges is now doubled. In order to maintain fundamental mode, the load should be changed to
The displacement of the particle at x = 0 of a stretched string carrying a wave in the positive x-direction is given f(t) = A sin (t/T). The wave speed is v. Write the wave equation.
The equation of a wave travelling on a string is \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 10 \text{ mm } \right) \sin\left[ \left( 31 \cdot 4 m^{- 1} \right)x + \left( 314 s^{- 1} \right)t \right]\]
(a) In which direction does the wave travel? (b) Find the wave speed, the wavelength and the frequency of the wave. (c) What is the maximum displacement and the maximum speed of a portion of the string?
A 200 Hz wave with amplitude 1 mm travels on a long string of linear mass density 6 g m−1 kept under a tension of 60 N. (a) Find the average power transmitted across a given point on the string. (b) Find the total energy associated with the wave in a 2⋅0 m long portion of the string.
Two waves, travelling in the same direction through the same region, have equal frequencies, wavelengths and amplitudes. If the amplitude of each wave is 4 mm and the phase difference between the waves is 90°, what is the resultant amplitude?
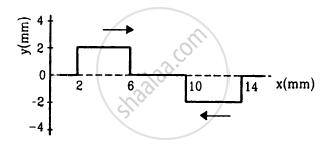
Following figure shows two wave pulses at t = 0 travelling on a string in opposite directions with the same wave speed 50 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 4 ms, 6 ms, 8 ms, and 12 ms.
A 40 cm wire having a mass of 3⋅2 g is stretched between two fixed supports 40⋅05 cm apart. In its fundamental mode, the wire vibrates at 220 Hz. If the area of cross section of the wire is 1⋅0 mm2, find its Young modulus.
What is the interference of sound waves?
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
Speed of sound wave in air ______.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
