Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. The minimum distance between the two particles, always having same speed, is
Options
\[\lambda/4\]
\[\lambda/3\]
\[\lambda/2\]
\[\lambda\]
Solution
\[\lambda/2\]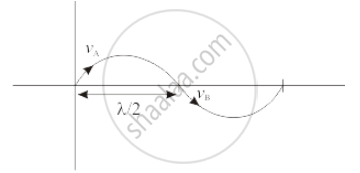
A sine wave has a maxima and a minima and the particle displacement has phase difference of π radians. The speeds at the maximum point and at the minimum point are same although the direction of motion are different. The difference between the positions of maxima and minima is equal to
\[\lambda/2\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For the wave described in Exercise 15.8, plot the displacement (y) versus (t) graphs for x = 0, 2 and 4 cm. What are the shapes of these graphs? In which aspects does the oscillatory motion in travelling wave differ from one point to another: amplitude, frequency or phase?
(i) For the wave on a string described in Exercise 15.11, do all the points on the string oscillate with the same (a) frequency, (b) phase, (c) amplitude? Explain your answers. (ii) What is the amplitude of a point 0.375 m away from one end?
A steel rod 100 cm long is clamped at its middle. The fundamental frequency of longitudinal vibrations of the rod is given to be 2.53 kHz. What is the speed of sound in steel?
Show that for a wave travelling on a string
\[\frac{y_{max}}{\nu_{max}} = \frac{\nu_{max}}{\alpha_{max}},\]
where the symbols have usual meanings. Can we use componendo and dividendo taught in algebra to write
\[\frac{y_{max} + \nu_{max}}{\nu_{max} - \nu_{max}} = \frac{\nu_{max} + \alpha_{max}}{\nu_{max} - \alpha_{max}}?\]
A sine wave is travelling in a medium. A particular particle has zero displacement at a certain instant. The particle closest to it having zero displacement is at a distance
Velocity of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Its velocity in vacuum will be
A wave pulse, travelling on a two-piece string, gets partially reflected and partially transmitted at the junction. The reflected wave is inverted in shape as compared to the incident one. If the incident wave has wavelength λ and the transmitted wave λ'
Two waves of equal amplitude A, and equal frequency travel in the same direction in a medium. The amplitude of the resultant wave is
A wave pulse is travelling on a string with a speed \[\nu\] towards the positive X-axis. The shape of the string at t = 0 is given by g(x) = Asin(x/a), where A and a are constants. (a) What are the dimensions of A and a ? (b) Write the equation of the wave for a general time t, if the wave speed is \[\nu\].
The equation of a wave travelling on a string is \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 10 \text{ mm } \right) \sin\left[ \left( 31 \cdot 4 m^{- 1} \right)x + \left( 314 s^{- 1} \right)t \right]\]
(a) In which direction does the wave travel? (b) Find the wave speed, the wavelength and the frequency of the wave. (c) What is the maximum displacement and the maximum speed of a portion of the string?
A wave travelling on a string at a speed of 10 m s−1 causes each particle of the string to oscillate with a time period of 20 ms. (a) What is the wavelength of the wave? (b) If the displacement of a particle of 1⋅5 mm at a certain instant, what will be the displacement of a particle 10 cm away from it at the same instant?
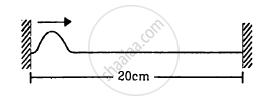
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0⋅40 g cm−1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an ends as shown in the figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a).
Two long strings A and B, each having linear mass density
\[1 \cdot 2 \times {10}^{- 2} kg m^{- 1}\] , are stretched by different tensions 4⋅8 N and 7⋅5 N respectively and are kept parallel to each other with their left ends at x = 0. Wave pulses are produced on the strings at the left ends at t = 0 on string A and at t = 20 ms on string B. When and where will the pulse on B overtake that on A?
What is the interference of sound waves?
A string of mass 2.5 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, the disturbance will reach the other end in ______.
Speed of sound waves in a fluid depends upon ______.
- directty on density of the medium.
- square of Bulk modulus of the medium.
- inversly on the square root of density.
- directly on the square root of bulk modulus of the medium.
A steel wire has a length of 12 m and a mass of 2.10 kg. What will be the speed of a transverse wave on this wire when a tension of 2.06 × 104N is applied?
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
