Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
∆ABC ~ ∆PBQ. In ∆ABC, AB = 3 cm, ∠B = 90°, BC = 4 cm. Ratio of the corresponding sides of two triangles is 7 : 4. Then construct ∆ABC and ∆PBQ
Solution

Analysis: As shown in the figure,
Let B–A–P and B–C–Q.
∆PBQ ∼ ∆ABC
∴ ∠PQB ≅ ∠ACB .....[Corresponding angles of similar triangles]
`"PB"/"AB" = "BQ"/"BC" = "PQ"/"AC"` .....(i) [Corresponding sides of similar triangles]
∴ `"PB"/"AB" = "BQ"/"BC" = "PQ"/"AC" = 7/4` ......[Given]
∴ Sides of ∆PBQ are longer than corresponding sides of ∆ABC.
∴ If seg BC is divided into 4 equal parts, then seg BQ will be 7 times each part of seg BC.
So, if we construct ∆ABC point Q will be on side BC, at a distance equal to 7 parts from B.
Now, point P is the point of intersection of ray AB and a line through Q, parallel to AC.
∴ ∆PBQ is the required triangle similar to ∆ABC.
Steps of construction:
- Draw seg BC of length 4 cm.
- Take ∠B as 90° and draw an arc of 3 cm on it. Name the point as A.
- Join seg AC to obtain ∆ABC.
- Draw ray BX such that ∠CBX is an acute angle.
- Locate points B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7 on ray BX such that, BB1 = B1B2 = B2B3 = B3B4 = B4B5 = B5B6 = B6B7.
- Join point C and B4.
- Through point, B7 draw a line parallel to seg CB4 which intersects seg BC at point Q.
- Draw a line parallel to AC through Q to intersect line AB at point P.
∆PBQ is the required triangle similar to ∆ABC.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
ΔRST ~ ΔUAY, In ΔRST, RS = 6 cm, ∠S = 50°, ST = 7.5 cm. The corresponding sides of ΔRST and ΔUAY are in the ratio 5 : 4. Construct ΔUAY.
Construct the circumcircle and incircle of an equilateral triangle ABC with side 6 cm and centre O. Find the ratio of radii of circumcircle and incircle.
Construct a Δ ABC in which AB = 6 cm, ∠A = 30° and ∠B = 60°, Construct another ΔAB’C’ similar to ΔABC with base AB’ = 8 cm.
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points A(3,- 3) and B(- 2, 7) is divided by x-axis. Also find the coordinates of the point of division.
Construct a triangle of sides 4 cm, 5cm and 6cm and then a triangle similar to it whose sides are `2/3` of the corresponding sides of the first triangle. Give the justification of the construction.
Construct a triangle with sides 5 cm, 6 cm and 7 cm and then another triangle whose sides are `7/5` of the corresponding sides of the first triangle. Give the justification of the construction.
Draw a right triangle in which the sides (other than hypotenuse) are of lengths 4 cm and 3 cm. the construct another triangle whose sides are `5/3` times the corresponding sides of the given triangle. Give the justification of the construction.
Draw a line segment of length 7 cm and divide it internally in the ratio 2 : 3.
Construct a triangle similar to a given ΔABC such that each of its sides is (5/7)th of the corresponding sides of Δ ABC. It is given that AB = 5 cm, BC = 7 cm and ∠ABC = 50°.
Construct a triangle similar to a given ΔABC such that each of its sides is (2/3)rd of the corresponding sides of ΔABC. It is given that BC = 6 cm, ∠B = 50° and ∠C = 60°.
Draw a ∆ABC in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm and AC = 6 cm. Then construct another triangle whose sides are\[\frac{3}{5}\] of the corresponding sides of ∆ABC ?
Find the ratio in which point T(–1, 6)divides the line segment joining the points P(–3, 10) and Q(6, –8).
Find the ratio in which point P(k, 7) divides the segment joining A(8, 9) and B(1, 2). Also find k.
Find the co-ordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment AB with A(2, 7) and B(–4, –8).
Δ SHR ∼ Δ SVU. In Δ SHR, SH = 4.5 cm, HR = 5.2 cm, SR = 5.8 cm and
SHSV = 53 then draw Δ SVU.
Draw a right triangle in which the sides (other than the hypotenuse) are of lengths 4 cm and 3 cm. Now construct another triangle whose sides are \[\frac{3}{5}\] times the corresponding sides of the given triangle.
Δ AMT ∼ ΔAHE. In Δ AMT, MA = 6.3 cm, ∠MAT = 120°, AT = 4.9 cm, `(MA)/(HA) = 7/5`. construct Δ AHE.
Choose the correct alternative:
______ number of tangents can be drawn to a circle from the point on the circle.
Construct an equilateral ∆ABC with side 5 cm. ∆ABC ~ ∆LMN, ratio the corresponding sides of triangle is 6 : 7, then construct ΔLMN and ΔABC
If the point P (6, 7) divides the segment joining A(8, 9) and B(1, 2) in some ratio, find that ratio
Solution:
Point P divides segment AB in the ratio m: n.
A(8, 9) = (x1, y1), B(1, 2 ) = (x2, y2) and P(6, 7) = (x, y)
Using Section formula of internal division,
∴ 7 = `("m"(square) - "n"(9))/("m" + "n")`
∴ 7m + 7n = `square` + 9n
∴ 7m – `square` = 9n – `square`
∴ `square` = 2n
∴ `"m"/"n" = square`
To divide a line segment AB in the ratio 4 : 7, a ray AX is drawn first such that ∠BAX is an acute angle and then points A1, A2, A3, .... are located at equal distances on the ray AX and the point B is joined to ______.
To construct a triangle similar to a given ΔABC with its sides `3/7` of the corresponding sides of ΔABC, first draw a ray BX such that ∠CBX is an acute angle and X lies on the opposite side of A with respect to BC. Then locate points B1, B2, B3, ... on BX at equal distances and next step is to join ______.
By geometrical construction, it is possible to divide a line segment in the ratio ______.
A rhombus ABCD in which AB = 4cm and ABC = 60o, divides it into two triangles say, ABC and ADC. Construct the triangle AB’C’ similar to triangle ABC with scale factor `2/3`. Select the correct figure.
For ∆ABC in which BC = 7.5cm, ∠B =45° and AB - AC = 4, select the correct figure.
To divide a line segment PQ in the ratio 5 : 7, first a ray PX is drawn so that ∠QPX is an acute angle and then at equal distances points are marked on the ray PX such that the minimum number of these points is ______.
When a line segment is divided in the ratio 2 : 3, how many parts is it divided into?
If the perpendicular distance between AP is given, which vertices of the similar triangle would you find first?
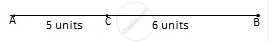
A point C divides a line segment AB in the ratio 5 : 6. The ratio of lengths AB: BC is ______.
What is the ratio `(AC)/(BC)` for the line segment AB following the construction method below?
Step 1: A ray is extended from A and 30 arcs of equal lengths are cut, cutting the ray at A1, A2,…A30
Step 2: A line is drawn from A30 to B and a line parallel to A30B is drawn, passing through the point A17 and meet AB at C.
The basic principle used in dividing a line segment is ______.
Draw a triangle ABC in which BC = 6 cm, CA = 5 cm and AB = 4 cm. Construct a triangle similar to it and of scale factor `5/3`.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠ABC = 60°. Construct a triangle similar to ∆ABC with scale factor `5/7`. Justify the construction.
Draw a triangle ABC in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 9 cm. Construct a triangle similar to ∆ABC with scale factor `3/2`. Justify the construction. Are the two triangles congruent? Note that all the three angles and two sides of the two triangles are equal.
