Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
Solution
(a) larger wavelength
(c) larger velocity
The velocity varies with temperature as \[v \propto \sqrt{T}\].Therefore, it increases. Since the frequency remains constant, the wavelength will increase as \[\lambda \propto v\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
Can you hear your own words if you are standing in a perfect vacuum? Can you hear your friend in the same conditions?
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
At what temperature will the speed of sound be double of its value at 0°C?
The absolute temperature of air in a region linearly increases from T1 to T2 in a space of width d. Find the time taken by a sound wave to go through the region in terms of T1, T2, d and the speed v of sound at 273 K. Evaluate this time for T1 = 280 K, T2 = 310 K, d = 33 m and v = 330 m s−1.
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A string, fixed at both ends, vibrates in a resonant mode with a separation of 2⋅0 cm between the consecutive nodes. For the next higher resonant frequency, this separation is reduced to 1⋅6 cm. Find the length of the string.
Three sources of sound S1, S2 and S3 of equal intensity are placed in a straight line with S1S2 = S2S3. At a point P, far away from the sources, the wave coming from S2 is 120° ahead in phase of that from S1. Also, the wave coming from S3 is 120° ahead of that from S2. What would be the resultant intensity of sound at P?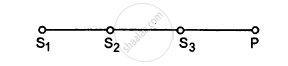
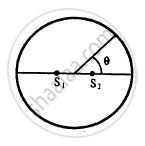
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
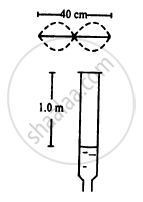
Consider the situation shown in the figure.The wire which has a mass of 4.00 g oscillates in its second harmonic and sets the air column in the tube into vibrations in its fundamental mode. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the tension in the wire.
A source of sound with adjustable frequency produces 2 beats per second with a tuning fork when its frequency is either 476 Hz of 480 Hz. What is the frequency of the tuning fork?
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A car moves with a speed of 54 km h−1 towards a cliff. The horn of the car emits sound of frequency 400 Hz at a speed of 335 m s−1. (a) Find the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn in front of the car. (b) Find the wavelength of the wave reflected from the cliff. (c) What frequency does a person sitting in the car hear for the reflected sound wave? (d) How many beats does he hear in 10 seconds between the sound coming directly from the horn and that coming after the reflection?
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
With propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium, the quantity transmitted is ______.
