Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose correct alternatives :
The direction cosines of the normal to the plane 2x – y + 2z = 3 are ______
Options
`(2)/(3),(-1)/(3),(2)/(3)`
`(-2)/(3),(1)/(3),(-2)/(3)`
`(2)/(3),(1)/(3),(2)/(3)`
`(2)/(3),(-1)/(3),(-2)/(3)`
Solution
`(2)/(3),(-1)/(3),(2)/(3)`
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the perpendicular distance of the point (1, 0, 0) from the line `(x - 1)/(2) = (y + 1)/(-3) = (z + 10)/(8)` Also find the co-ordinates of the foot of the perpendicular.
If the lines `(x - 1)/2 = (y + 1)/3 = (z - 1)/4 and (x - 3)/1 = (y - k)/2 = z/1` intersect each other, then find k.
Find the perpendicular distance of the origin from the plane 6x – 2y + 3z – 7 = 0.
Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane 2x + 6y – 3z = 63.
Reduce the equation `bar"r".(3hat"i" + 4hat"j" + 12hat"k")` to normal form and hence find
(i) the length of the perpendicular from the origin to the plane
(ii) direction cosines of the normal.
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the point having position vector `hati + hatj + hatk` and perpendicular to the vector `4hati + 5hatj + 6hatk`.
Find the co-ordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the point (0, 2, 3) to the line `(x + 3)/(5) = (y - 1)/(2) = (z + 4)/(3)`.
Choose correct alternatives :
If the line `x/(3) = y/(4)` = z is perpendicular to the line `(x - 1)/k = (y + 2)/(3) = (z - 3)/(k - 1)`, then the value of k is
Choose correct alternatives :
The length of the perpendicular from (1, 6,3) to the line `x/(1) = (y - 1)/(2) =(z - 2)/(3)`
Choose correct alternatives :
Equation of X-axis is ______.
The perpendicular distance of the plane 2x + 3y – z = k from the origin is `sqrt(14)` units, the value of k is ______.
If the planes 2x – my + z = 3 and 4x – y + 2z = 5 are parallel then m = ______
If the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane is (4, −2, -5), then the equation of the plane is ______
Find the direction ratios of the normal to the plane 2x + 3y + z = 7
If the normal to the plane has direction ratios 2, −1, 2 and it’s perpendicular distance from origin is 6, find its equation
Find the perpendicular distance of origin from the plane 6x − 2y + 3z - 7 = 0
Find the vector equation of a plane at a distance 6 units from the origin and to which vector `2hat"i" - hat"j" + 2hat"k"` is normal
Find the vector equation of the plane which bisects the segment joining A(2, 3, 6) and B(4, 3, −2) at right angles
If z1 and z2 are z-coordinates of the points of trisection of the segment joining the points A (2, 1, 4), B (–1, 3, 6) then z1 + z2 = ______.
The equation of the plane passing through the point (– 1, 2, 1) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (– 3, 1, 2) and (2, 3, 4) is ______.
Equation of plane parallel to ZX-plane and passing through the point (0, 5, 0) is ______
The equation of the plane, which bisects the line joining the points (1, 2, 3) and (3, 4, 5) at right angles is ______
A plane which passes through the point (3, 2, 0) and the line `(x - 3)/1 = (y - 6)/5, (z - 4)/4` is ______
Find the coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane 3y + 5 = 0.
The equation of the plane through the line x + y + z + 3 = 0 = 2x – y + 3z + 1 and parallel to the line `x/1 = y/2 = z/3`, is ______.
What will be the equation of plane passing through a point (1, 4, – 2) and parallel to the given plane – 2x + y – 3z = 9?
If the foot of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane is (4, –2, 5), then the equation of the plane is ______.
Find the equation of the plane containing the lines `(x - 1)/2 = (y + 1)/-1 = z/3` and `x/2 = (y - 2)/-1 = (z + 1)/3`.
Find the equation of plane which is at a distance of 4 units from the origin and which is normal to the vector `2hati - 2hatj + hatk`.
The coordinates of the foot of the perpendicular from the point P(1, 0, 0) in the line `(x - 1)/2 = (y + 1)/-3 = (z + 10)/8` are ______.
Find the point of intersection of the line `(x + 1)/2 = (y - 1)/3 = (z - 2)/1` with the plane x + 2y – z = 6.
A mobile tower is situated at the top of a hill. Consider the surface on which the tower stands as a plane having points A(1, 0, 2), B(3, –1, 1) and C(1, 2, 1) on it. The mobile tower is tied with three cables from the points A, B and C such that it stands vertically on the ground. The top of the tower is at point P(2, 3, 1) as shown in the figure below. The foot of the perpendicular from the point P on the plane is at the point `Q(43/29, 77/29, 9/29)`.
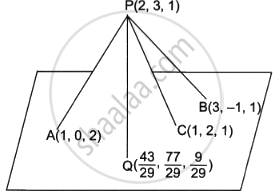
Answer the following questions.
- Find the equation of the plane containing the points A, B and C.
- Find the equation of the line PQ.
- Calculate the height of the tower.
