Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
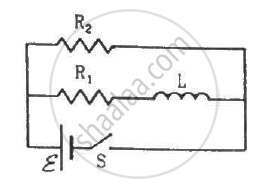
Consider the circuit shown in figure. (a) Find the current through the battery a long time after the switch S is closed. (b) Suppose the switch is again opened at t = 0. What is the time constant of the discharging circuit? (c) Find the current through the inductor after one time constant.
Solution
(a) Because the switch is closed, the battery gets connected across the L‒R circuit.
The current in the L‒R circuit after t seconds after connecting the battery is given by
i = i0 (1 − e−t/τ)
Here,
i0 = Steady state current
τ = Time constant = `L/R`
After a long time, t → ∞.
Now,
Current in the inductor, i = i0 (1 − e0) = 0
Thus, the effect of inductance vanishes.
\[i = \frac{\epsilon}{R_{net}}\]
\[i = \frac{\epsilon}{\frac{R_1 \times R_2}{R_1 + R_2}} = \frac{\epsilon( R_1 + R_2 )}{R_1 R_2}\]
(b) When the switch is opened, the resistance are in series.
The time constant is given by
\[\tau = \frac{L}{R_{net}} = \frac{L}{R_1 + R_2}\]
(c) The inductor will discharge through resistors R1 and R2.
The current through the inductor after one time constant is given by
t = τ
∴ Current, i = i0 e−τ/τ
Here,
\[i_0=\frac{\epsilon}{R_1 + R_2}\]
\[\therefore i=\frac{\epsilon}{R_1 + R_2} \times \frac{1}{e}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a series LCR circuit, VL = VC ≠ VR. What is the value of power factor?
A series LCR circuit is connected across an a.c. source of variable angular frequency 'ω'. Plot a graph showing variation of current 'i' as a function of 'ω' for two resistances R1 and R2 (R1 > R2).
Answer the following questions using this graph :
(a) In which case is the resonance sharper and why?
(b) In which case in the power dissipation more and why?
An LR circuit contains an inductor of 500 mH, a resistor of 25.0 Ω and an emf of 5.00 V in series. Find the potential difference across the resistor at t = (a) 20.0 ms, (b) 100 ms and (c) 1.00 s.
An LR circuit having a time constant of 50 ms is connected with an ideal battery of emf ε. find the time elapsed before (a) the current reaches half its maximum value, (b) the power dissipated in heat reaches half its maximum value and (c) the magnetic field energy stored in the circuit reaches half its maximum value.
The current in a discharging LR circuit without the battery drops from 2.0 A to 1.0 A in 0.10 s. (a) Find the time constant of the circuit. (b) If the inductance of the circuit 4.0 H, what is its resistance?
The potential difference across the resistor is 160V and that across the inductor is 120V. Find the effective value of the applied voltage. If the effective current in the circuit be 1.0 A, calculate the total impedance of the circuit.
Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the current flowing in an ideal inductor connected to an a.c. source of voltage, v= vo sin ωt. Hence plot graphs showing the variation of (i) applied voltage and (ii) the current as a function of ωt.
Choose the correct answer from given options
The selectivity of a series LCR a.c. circuit is large, when
A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 µF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
In a series LCR circuit supplied with AC, ______.
In series combination of R, L and C with an A.C. source at resonance, if R = 20 ohm, then impedence Z of the combination is ______.
Assertion: When the frequency of the AC source in an LCR circuit equals the resonant frequency, the reactance of the circuit is zero, and so there is no current through the inductor or the capacitor.
Reason: The net current in the inductor and capacitor is zero.
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator
Which of the following components of an LCR circuit, with a.c. supply, dissipates energy?
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is ______.
Which of the following combinations should be selected for better tuning of an LCR circuit used for communication?
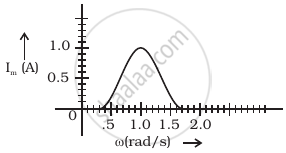
In series LCR circuit, the plot of Imax vs ω is shown in figure. Find the bandwidth and mark in the figure.
A series RL circuit with R = 10 Ω and L = `(100/pi)` mH is connected to an ac source of voltage V = 141 sin (100 πt), where V is in volts and t is in seconds. Calculate
- the impedance of the circuit
- phase angle, and
- the voltage drop across the inductor.
An alternating voltage of 220 V is applied across a device X. A current of 0.22 A flows in the circuit and it lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the current in the circuit remains the same and it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y and,
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
Three students, X, Y and Z performed an experiment for studying the variation of a.c. with frequency in a series LCR circuit and obtained the graphs as shown below. They all used
- an AC source of the same emf and
- inductance of the same value.
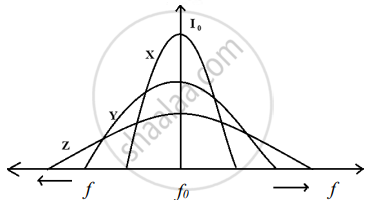
- Who used minimum resistance?
- In which case will the quality Q factor be maximum?
- What did the students conclude about the nature of impedance at resonant frequency (f0)?
- An ideal capacitor is connected across 220V, 50Hz, and 220V, 100Hz supplies. Find the ratio of current flowing through it in the two cases.
