Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
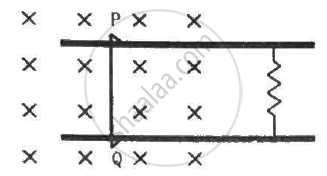
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wires P1Q1 and P2Q2 are made to slide on the rails with the same speed 5 cm s−1. Suppose the 19 Ω resistor is disconnected. Find the current through P2Q2 if (a) both the wires move towards right and (b) if P1Q1 moves towards left but P2Q2 moves towards right.

Solution
(a) When the wires move in the same direction, their polarity remains the same. The circuit remains incomplete. Therefore, no current flows in the circuit.
(b) When the wires move in opposite directions, their polarities are reversed. Thus, current flows in the circuit.
\[V_{P_2 Q_2} = Blv\]
= 1 × 0.04 × 0.05
= 2 × 10−3 V
R = 2 Ω
Current in the circuit is given by
\[i = \frac{2 \times {10}^{- 3}}{2}\]
= 1 × 10−3 A = 1 mA
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the condition under which the charged particles moving with different speeds in the presence of electric and magnetic field vectors can be used to select charged particles of a particular speed.
Two identical coils P and Q each of radius R are lying in perpendicular planes such that they have a common centre. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at the common centre of the two coils, if they carry currents equal to I and \[\sqrt{3}\] I respectively.

A point charge q moving with speed v enters a uniform magnetic field B that is acting into the plane of the paper as shown. What is the path followed by the charge q and in which plane does it move?
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting oscillating electric and magnetic fields of an em wave propagating along + z-direction ?
Show with the help of a diagram how the force between the two conductors would change when the currents in them flow in the opposite directions?
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying steady currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance 'd'. Explain briefly, with the help of a suitable diagram, how the magnetic field due to one conductor acts on the other. Hence deduce the expression for the force acting between the two conductors. Mention the nature of this force.
Two proton beams going in the same direction repel each other whereas two wires carrying currents in the same direction attract each other. Explain.
A moving charge produces
Consider the situation shown in figure. The wire PQ has mass m, resistance r and can slide on the smooth, horizontal parallel rails separated by a distance l. The resistance of the rails is negligible. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the rectangular region and a resistance R connects the rails outside the field region. At t = 0, the wire PQ is pushed towards right with a speed v0. Find (a) the current in the loop at an instant when the speed of the wire PQ is v, (b) the acceleration of the wire at this instant, (c) the velocity vas a functions of x and (d) the maximum distance the wire will move.
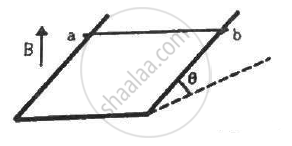
A wire ab of length l, mass m and resistance R slides on a smooth, thick pair of metallic rails joined at the bottom as shown in figure. The plane of the rails makes an angle θ with the horizontal. A vertical magnetic field B exists in the region. If the wire slides on the rails at a constant speed v, show that \[B = \sqrt{\frac{mg R sin\theta}{v l^2 \cos^2 \theta}}\]
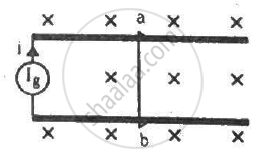
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. Find the velocity of the wire as a function of time.
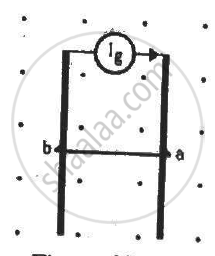
The current generator Ig' shown in figure, sends a constant current i through the circuit. The wire ab has a length l and mass m and can slide on the smooth, horizontal rails connected to Ig. The entire system lies in a vertical magnetic field B. The system is kept vertically in a uniform horizontal magnetic field B that is perpendicular to the plane of the rails (figure). It is found that the wire stays in equilibrium. If the wire ab is replaced by another wire of double its mass, how long will it take in falling through a distance equal to its length?
A magnetic field that varies in magnitude from point to point but has a constant direction (east to west) is set up in a chamber. A charged particle enters the chamber and travels undeflected along a straight path with constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle?
A charged particle moves through a magnetic field perpendicular to its direction. Then ______.
A moving charge will gain kinetic energy due to the application of ______.
A conductor ABOCD moves along its bisector with a velocity 1 m/s through a perpendicular magnetic field of 1 wb/m2, as shown in figure. If all the four sides are 1 m length each, then the induced emf between A and Din approx is ______V.

An α particle is moving along a circle of radius R with a constant angular velocity ω. Point A lies in the same plane at a distance 2R from the centre. Point A records magnetic field produced by α particle, if the minimum time interval between two successive times at which A records zero magnetic field is 't' the angular speed ω, in terms of t is ______.
