Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
D is a point in side BC of triangle ABC. If AD > AC, show that AB > AC.
Solution
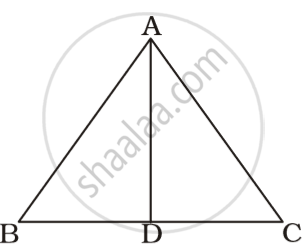
In ΔADC
AD > AC
⇒ ∠ACD > ∠ADC ...(i)
In ΔABD
∠ABD + ∠BAD = ∠ADC ...(ii)
Putting the value of ∠ADC in equation (i)
∠ACD > ∠ABD + ∠BAD ...(iii)
⇒ ∠ACD > ∠ABD
⇒ ∠ACB > ∠ABC
AB > AC
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
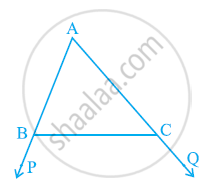
In the given figure sides AB and AC of ΔABC are extended to points P and Q respectively. Also, ∠PBC < ∠QCB. Show that AC > AB.
Show that of all line segments drawn from a given point not on it, the perpendicular line segment is the shortest.
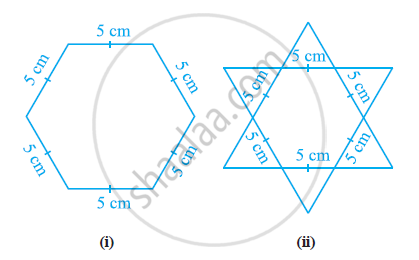
Complete the hexagonal and star shaped rangolies (see the given figures) by filling them with as many equilateral triangles of side 1 cm as you can. Count the number of triangles in each case. Which has more triangles?
In a triangle PQR; QR = PR and ∠P = 36o. Which is the largest side of the triangle?
Arrange the sides of ∆BOC in descending order of their lengths. BO and CO are bisectors of angles ABC and ACB respectively.
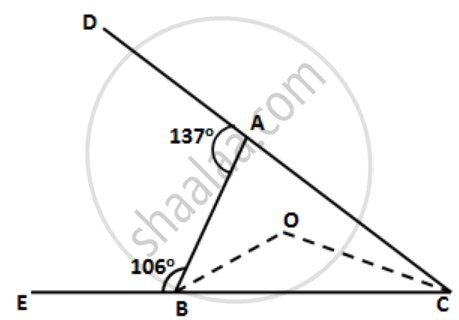
In the following figure, write BC, AC, and CD in ascending order of their lengths.
Name the smallest angle in each of these triangles:
In ΔXYZ, XY = 6.2cm, XY = 6.8cm and YZ = 5cm
D is a point on the side of the BC of ΔABC. Prove that the perimeter of ΔABC is greater than twice of AD.
ABCD is a trapezium. Prove that: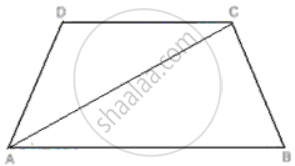
CD + DA + AB > BC.
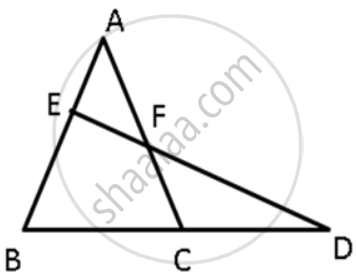
ΔABC in a isosceles triangle with AB = AC. D is a point on BC produced. ED intersects AB at E and AC at F. Prove that AF > AE.