Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
Solution
p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure:

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
Draw a p-V diagram showing negative work with varying pressure.
State the assumptions made for thermodynamic processes.
3 mole of a gas at temperature 400 K expands isothermally from an initial volume of 4 litres to a final volume of 8 litres. Find the work done by the gas. (R = 8.31 J mol-1 K-1)
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
The V-T diagram of an ideal gas which goes through a reversible cycle A→B→C→D is shown below. (Processes D→A and B→C are adiabatic)
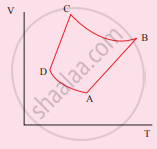
The corresponding PV diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic)
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
Apply first law for an isobaric process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isochoric process.
Derive the work done in an adiabatic process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
In a petrol engine, (internal combustion engine) air at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 20°C is compressed in the cylinder by the piston to `1/8` of its original volume. Calculate the temperature of the compressed air. (For air γ = 1.4)
For a given ideal gas 6 × 105 J heat energy is supplied and the volume of gas is increased from 4 m3 to 6 m3 at atmospheric pressure. Calculate
- the work done by the gas
- change in internal energy of the gas
- graph this process in PV and TV diagram
A monoatomic gas of pressure p having volume V expands isothermally to a volume 2V and then adiabatically to a volume 16V. The final pressure of the gas is ____________.
`("ratio of specific heats" = 5/3)`
One mole of an ideal gas with `gamma` = 1.4 is adiabatically compressed so that its temperature rises from 27° C to 47° C. The change in the internal energy of the gas is (R = 8.3 J/mol.K) ____________.
Two identical samples of a gas are allowed to expand (i) isothermally (ii) adiabatically. Work done is ____________.
Assertion: Equal volumes of monatomic and polyatomic gases are adiabatically compressed separately to equal compression ratio `("P"_2/"P"_1)`. Then monatomic gas will have greater final volume.
Reason: Among ideal gases, molecules of a monatomic gas have the smallest number of degrees of freedom.
Which of the following processes is reversible?
Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in figure.
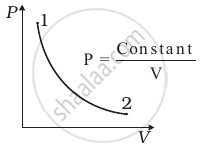
Out of the following diagrams (figure), which represents the T-P diagram?
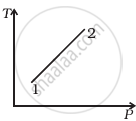 (i) |
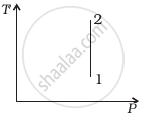 (ii) |
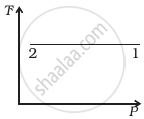 (iii) |
 (iv) |
In a certain thermodynamical process, the pressure of a gas depends on its volume as kV3. The work done when the temperature changes from 100°C to 300°C will be ______ nR, where n denotes number of moles of a gas.
Explain the thermodynamic process.
In a cyclic process, if ΔU = internal energy, W = work done, Q = Heat supplied then ______.
