Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the equation of the line which passes through the point (− 4, 3) and the portion of the line intercepted between the axes is divided internally in the ratio 5 : 3 by this point.
Solution
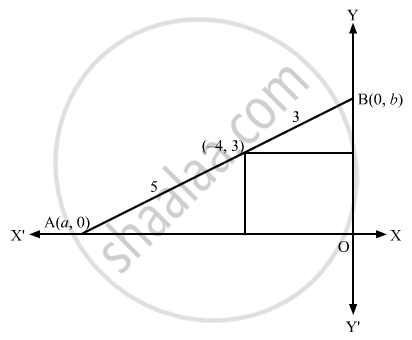
The x - coordinate of the point A is given by
\[- 4 = \frac{3 \times a + 5 \times 0}{3 + 5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{- 32}{3}\]
The y - coordinate of the point B is given by
\[3 = \frac{3 \times 0 + 5 \times b}{3 + 5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \frac{24}{5}\]
The equation of the line passing is given by
\[\frac{x}{\frac{- 32}{3}} + \frac{y}{\frac{24}{5}} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow 9x - 20y + 96 = 0\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the equation of the line perpendicular to x-axis and having intercept − 2 on x-axis.
Find the equation of the line passing through \[(2, 2\sqrt{3})\] and inclined with x-axis at an angle of 75°.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point (1,2) and makes such an angle with the positive direction of x-axis whose sine is \[\frac{3}{5}\].
Find the equation of the line passing through the point (−3, 5) and perpendicular to the line joining (2, 5) and (−3, 6).
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the following pair of point :
(0, 0) and (2, −2)
Find the equation of the straight lines passing through the following pair of point :
(at1, a/t1) and (at2, a/t2)
Find the equations of the sides of the triangles the coordinates of whose angular point is respectively (0, 1), (2, 0) and (−1, −2).
The length L (in centimeters) of a copper rod is a linear function of its celsius temperature C. In an experiment, if L = 124.942 when C = 20 and L = 125.134 when C = 110, express L in terms of C.
Find the equations to the straight lines which go through the origin and trisect the portion of the straight line 3 x + y = 12 which is intercepted between the axes of coordinates.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through (1, −2) and cuts off equal intercepts on the axes.
Find the equation to the straight line which cuts off equal positive intercepts on the axes and their product is 25.
A straight line passes through the point (α, β) and this point bisects the portion of the line intercepted between the axes. Show that the equation of the straight line is \[\frac{x}{2 \alpha} + \frac{y}{2 \beta} = 1\].
Find the equations of the straight lines each of which passes through the point (3, 2) and cuts off intercepts a and b respectively on X and Y-axes such that a − b = 2.
Find the equations of the straight lines which pass through the origin and trisect the portion of the straight line 2x + 3y = 6 which is intercepted between the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point (2, 1) and bisecting the portion of the straight line 3x − 5y = 15 lying between the axes.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the origin and bisecting the portion of the line ax + by + c = 0 intercepted between the coordinate axes.
Find the equation of straight line passing through (−2, −7) and having an intercept of length 3 between the straight lines 4x + 3y = 12 and 4x + 3y = 3.
Three sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle ABC are 5x − 3y + 2 = 0, x − 3y − 2 = 0 and x + y − 6 = 0 respectively. Find the equation of the altitude through the vertex A.
Find the equation of the straight line passing through the point of intersection of the lines 5x − 6y − 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 5 = 0 and perpendicular to the line 3x − 5y + 11 = 0 .
Find the equation of the straight line through the point (α, β) and perpendicular to the line lx + my + n = 0.
Find the distance of the point (1, 2) from the straight line with slope 5 and passing through the point of intersection of x + 2y = 5 and x − 3y = 7.
Find the equations of the straight lines passing through (2, −1) and making an angle of 45° with the line 6x + 5y − 8 = 0.
Find the equations to the straight lines passing through the point (2, 3) and inclined at and angle of 45° to the line 3x + y − 5 = 0.
Find the equations to the sides of an isosceles right angled triangle the equation of whose hypotenues is 3x + 4y = 4 and the opposite vertex is the point (2, 2).
Find the equations of two straight lines passing through (1, 2) and making an angle of 60° with the line x + y = 0. Find also the area of the triangle formed by the three lines.
The equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and its vertex is (2, −1). Find the length and equations of its sides.
Show that the straight lines given by (2 + k) x + (1 + k) y = 5 + 7k for different values of k pass through a fixed point. Also, find that point.
Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point of intersection of the lines 3x − y = 5 and x + 3y = 1 and makes equal and positive intercepts on the axes.
Write the area of the triangle formed by the coordinate axes and the line (sec θ − tan θ) x + (sec θ + tan θ) y = 2.
Write the integral values of m for which the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the lines y = mx + 1 and 3x + 4y = 9 is an integer.
Find the locus of the mid-points of the portion of the line x sinθ+ y cosθ = p intercepted between the axes.
The equation of the line passing through (1, 5) and perpendicular to the line 3x − 5y + 7 = 0 is
Find the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection of 2x + y = 5 and x + 3y + 8 = 0 and parallel to the line 3x + 4y = 7.
The equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2) and perpendicular to the line x + y + 1 = 0 is ______.
Equation of the line passing through the point (a cos3θ, a sin3θ) and perpendicular to the line x sec θ + y cosec θ = a is x cos θ – y sin θ = a sin 2θ.
