Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In a college, 70% of students pass in Physics, 75% pass in Mathematics and 10% of students fail in both. One student is chosen at random. What is the probability that:
(i) He passes in Physics and Mathematics?
(ii) He passes in Mathematics given that he passes in Physics.
(iii) He passes in Physics given that he passes in Mathematics.
Solution
Let x% of students pass in both Physics and Mathematics
Students pass in Physics = 70% ⇒ P (P) = `(70)/(100)`
Students pass in Mathematics = 75% ⇒ P (M) = `(75)/(100)`
Students fail in both = 10%
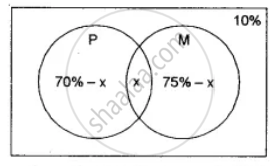
Now students pass in physics only + students pass in mathematics only + students pass in both physics and mathematics = 90%
⇒ 70% - x + x + 75% - x = 90%
x = 55% ⇒ P (M ∩ P) = `(55)/(100)`
(i)
P ( Passes in Physics and Mathematics) = `(55)/(100) = (11)/(20)`
(ii)
P (M/P) = `(P (M ∩ P))/(P(P)`
= `((55)/(100))/(70/(100))`
= `(55)/(70) = (11)/(14)`
(iii)
`P(P/M) = (P(M ∩ P))/(P(M))`
`(55/100)/(75/100)`
= `55/75 = 11/15`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
40% students of a college reside in hostel and the remaining reside outside. At the end of the year, 50% of the hostelers got A grade while from outside students, only 30% got A grade in the examination. At the end of the year, a student of the college was chosen at random and was found to have gotten A grade. What is the probability that the selected student was a hosteler ?
Evaluate P(A ∪ B), if 2P(A) = P(B) = `5/13` and P(A | B) = `2/5`
If `P(A) = 6/11, P(B) = 5/11 "and" P(A ∪ B) = 7/11` find
- P(A ∩ B)
- P(A|B)
- P(B|A)
Determine P(E|F).
A coin is tossed three times, where
E: at least two heads, F: at most two heads
Consider the experiment of throwing a die, if a multiple of 3 comes up, throw the die again and if any other number comes, toss a coin. Find the conditional probability of the event ‘the coin shows a tail’, given that ‘at least one die shows a 3’.
If P(A) = `1/2`, P(B) = 0, then P(A|B) is ______.
Suppose we have four boxes. A, B, C and D containing coloured marbles as given below:
| Box | Marble colour | ||
| Red | White | Black | |
| A | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| B | 6 | 2 | 2 |
| C | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| D | 0 | 6 | 4 |
One of the boxes has been selected at random and a single marble is drawn from it. If the marble is red, what is the probability that it was drawn from box A?, box B?, box C?
If A and B are events such as that P(A) = `1/2`, P(B) = `1/3` and P(A ∩ B) = `1/4`, then find
1) P(A / B)
2) P(B / A)
Three cards are drawn at random (without replacement) from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of red cards. Hence, find the mean of the distribution.
If events A and B are independent, such that `P(A)= 3/5`, `P(B)=2/3` 'find P(A ∪ B).
A pair of dice is thrown. If sum of the numbers is an even number, what is the probability that it is a perfect square?
A bag contains 10 white balls and 15 black balls. Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement. What is the probability that, first is white and second is black?
From a pack of well-shuffled cards, two cards are drawn at random. Find the probability that both the cards are diamonds when the first card drawn is replaced in the pack
Select the correct option from the given alternatives :
Bag I contains 3 red and 4 black balls while another Bag II contains 5 red and 6 black balls. One ball is drawn at random from one of the bags and it is found to be red. The probability that it was drawn from Bag II
If P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.8 and P(B/A) = 0.8, find P(A/B) and P(A ∪ B)
If for two events A and B, P(A) = `3/4`, P(B) = `2/5` and A ∪ B = S (sample space), find the conditional probability P(A/B)
Given P(A) = 0.4 and P(A ∪ B) = 0.7 Find P(B) if P(B/A) = 0.5
Choose the correct alternative:
If A and B are any two events, then the probability that exactly one of them occur is
Two dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of numbers appearing is more than 11, is ______.
If two balls are drawn from a bag containing 3 white, 4 black and 5 red balls. Then, the probability that the drawn balls are of different colours is:
A pack of cards has one card missing. Two cards are drawn randomly and are found to be spades. The probability that the missing card is not a spade, is ______.
If A and B are two events such that P(A) = `1/3`, P(B) = `1/5` and P(A ∪ B) = `1/2`, then P(A|B') + P(B|A') is equal to ______.
It is given that the events A and B are such that P(A) = `1/4, P(A/B) = 1/2` and `P(B/A) = 2/3`, then P(B) is equal to ______.
If the sum of numbers obtained on throwing a pair of dice is 9, then the probability that number obtained on one of the dice is 4, is ______.
If A and B are two independent events such that P(A) = `1/3` and P(B) = `1/4`, then `P(B^'/A)` is ______.
Three friends go to a restaurant to have pizza. They decide who will pay for the pizza by tossing a coin. It is decided that each one of them will toss a coin and if one person gets a different result (heads or tails) than the other two, that person would pay. If all three get the same result (all heads or all tails), they will toss again until they get a different result.
- What is the probability that all three friends will get the same result (all heads or all tails) in one round of tossing?
- What is the probability that they will get a different result in one round of tossing?
- What is the probability that they will need exactly four rounds of tossing to determine who would pay?
Students of under graduation submitted a case study on “Understanding the Probability of Left-Handedness in Children Based on Parental Handedness”. Following Recent studies suggest that roughly 12% of the world population is left-handed. Depending on the parents’ handedness, the chances of having a left-handed child are as follows:
Scenario A: Both parents are left-handed, with a 24% chance of the child being left-handed.
Scenario B: The fathers is right-handed and the mothers left-handed, with a 22% chance of child being left-handed.
Scenario C: The fathers left-handed and the mother is right-handed, with a 17% chance of child being left-handed.
Scenario D: Both parents are right-handed, with a 9% chance of having a left-handed child.
Assuming that scenarios A, B, C and D are equally likely and L denotes the event that the child is left-handed, answer the following questions.
- What is the overall probability that a randomly selected child is left-handed?
- Given that exactly one parent is left-handed, what is the probability that a randomly selected child is left-handed?
- If a child is left-handed, what is the probability that both parents are left-handed?
