Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the following figure, ABC is a right triangle right angled at A. BCED, ACFG and ABMN are squares on the sides BC, CA and AB respectively. Line segment AX ⊥ DE meets BC at Y. Show that:-
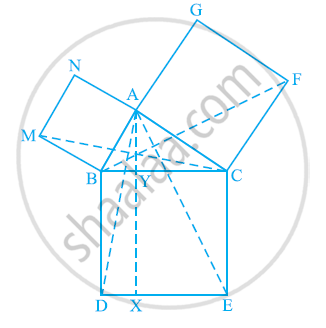
(i) ΔMBC ≅ ΔABD
(ii) ar (BYXD) = 2 ar(MBC)
(iii) ar (BYXD) = ar(ABMN)
(iv) ΔFCB ≅ ΔACE
(v) ar(CYXE) = 2 ar(FCB)
(vi) ar (CYXE) = ar(ACFG)
(vii) ar (BCED) = ar(ABMN) + ar(ACFG)
Note : Result (vii) is the famous Theorem of Pythagoras. You shall learn a simpler proof of this theorem in Class X.
Solution
(i) We know that each angle of a square is 90°.
Hence, ∠ABM = ∠DBC = 90º
⇒ ∠ABM + ∠ABC = ∠DBC + ∠ABC
⇒ ∠MBC = ∠ABD
In ΔMBC and ΔABD,
∠MBC = ∠ABD (Proved above)
MB = AB (Sides of square ABMN)
BC = BD (Sides of square BCED)
∴ ΔMBC ≅ ΔABD (SAS congruence rule)
(ii) We have
ΔMBC ≅ ΔABD
⇒ ar (ΔMBC) = ar (ΔABD) ... (1)
It is given that AX ⊥ DE and BD ⊥ DE (Adjacent sides of square
BDEC)
⇒ BD || AX (Two lines perpendicular to same line are parallel to each other)
ΔABD and parallelogram BYXD are on the same base BD and between the same parallels BD and AX.
∴ ar(ΔABD) = 1/2ar(BYXD)
ar(BYXD) = 2ar(ΔABD)
Area (BYXD) = 2 area (ΔMBC) [Using equation (1)] ... (2)
(iii) ΔMBC and parallelogram ABMN are lying on the same base MB and between same parallels MB and NC.
∴ ar(ΔMBC) = 1/2ar(ABMN)
2ar (ΔMBC) = ar (ABMN)
ar (BYXD) = ar (ABMN) [Using equation (2)] ... (3)
(iv) We know that each angle of a square is 90°.
∴ ∠FCA = ∠BCE = 90º
⇒ ∠FCA + ∠ACB = ∠BCE + ∠ACB
⇒ ∠FCB = ∠ACE
In ΔFCB and ΔACE,
∠FCB = ∠ACE
FC = AC (Sides of square ACFG)
CB = CE (Sides of square BCED)
ΔFCB ≅ ΔACE (SAS congruence rule)
(v) It is given that AX ⊥ DE and CE ⊥ DE (Adjacent sides of square BDEC)
Hence, CE || AX (Two lines perpendicular to the same line are parallel to each other)
Consider ΔACE and parallelogram CYXE
ΔACE and parallelogram CYXE are on the same base CE and between the same parallels CE and AX.
∴ ar(ΔACE) = 1/2ar(CYXE)
⇒ ar(CYXE) = 2 ar(ΔACE) ... (4)
We had proved that
∴ ΔFCB ≅ ΔACE
ar (ΔFCB) ≅ ar (ΔACE) ... (5)
On comparing equations (4) and (5), we obtain
ar (CYXE) = 2 ar (ΔFCB) ... (6)
(vi) Consider ΔFCB and parallelogram ACFG
ΔFCB and parallelogram ACFG are lying on the same base CF and between the same parallels CF and BG.
∴ ar(ΔFCB) = 1/2 ar(ACFG)
⇒ ar(ACFG) = 2 ar(ΔFCB)
⇒ ar (ACFG) = ar (CYXE) [Using equation (6)] ... (7)
(vii) From the figure, it is evident that
ar (BCED) = ar (BYXD) + ar (CYXE)
⇒ ar (BCED) = ar (ABMN) + ar (ACFG) [Using equations (3) and (7)]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Show that the diagonals of a parallelogram divide it into four triangles of equal area.
In the given figure, diagonals AC and BD of quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O such that OB = OD. If AB = CD, then show that:
(i) ar (DOC) = ar (AOB)
(ii) ar (DCB) = ar (ACB)
(iii) DA || CB or ABCD is a parallelogram.
[Hint: From D and B, draw perpendiculars to AC.]

XY is a line parallel to side BC of a triangle ABC. If BE || AC and CF || AB meet XY at E and F respectively, show that
ar (ABE) = ar (ACF)
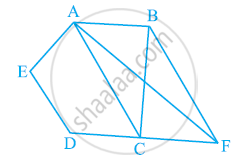
In the given figure, ABCDE is a pentagon. A line through B parallel to AC meets DC produced at F. Show that
(i) ar (ACB) = ar (ACF)
(ii) ar (AEDF) = ar (ABCDE)
A villager Itwaari has a plot of land of the shape of a quadrilateral. The Gram Panchayat of the village decided to take over some portion of his plot from one of the corners to construct a Health Centre. Itwaari agrees to the above proposal with the condition that he should be given equal amount of land in lieu of his land adjoining his plot so as to form a triangular plot. Explain how this proposal will be implemented.
In the given figure, AP || BQ || CR. Prove that ar (AQC) = ar (PBR).

PQRS is a parallelogram whose area is 180 cm2 and A is any point on the diagonal QS. The area of ∆ASR = 90 cm2.
ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid-point of BC. Then ar (BDE) = `1/4` ar (ABC).
The area of the parallelogram ABCD is 90 cm2 (see figure). Find
- ar (ΔABEF)
- ar (ΔABD)
- ar (ΔBEF)
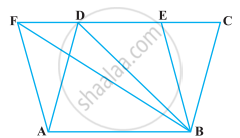
In the following figure, CD || AE and CY || BA. Prove that ar (CBX) = ar (AXY).

