Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
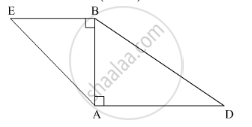
In the following figure, seg BE ⊥ seg AB and seg BA ⊥ seg AD. If BE = 6 and \[\text{AD} = 9 \text{ find} \frac{A\left( \Delta ABE \right)}{A\left( \Delta BAD \right)} \cdot\]
Solution

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
D is a point on the side BC of ∆ABC such that ∠ADC = ∠BAC. Prove that` \frac{"CA"}{"CD"}=\frac{"CB"}{"CA"} or "CA"^2 = "CB" × "CD".`
In an isosceles ∆ABC, the base AB is produced both ways in P and Q such that AP × BQ = AC2 and CE are the altitudes. Prove that ∆ACP ~ ∆BCQ.
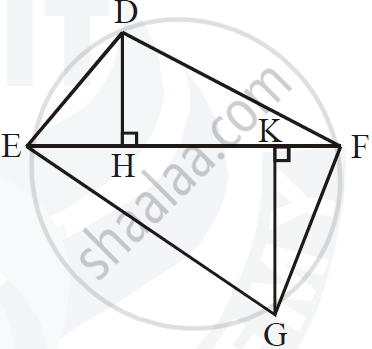
In the following figure, seg DH ⊥ seg EF and seg GK ⊥ seg EF. If DH = 18 cm, GK = 30 cm and `A(triangle DEF) = 450 cm^2`, then find:
1) EF
2) `A(triangle GFE)`
3) `A(square DFGE)`
The ratio between the corresponding sides of two similar triangles is 2 is to 5. Find the ratio between the areas of these triangles.
In the given figure, if ∠ADE = ∠B, show that ΔADE ~ ΔABC. If AD = 3.8cm, AE = 3.6cm, BE = 2.1cm and BC = 4.2cm, find DE.
The corresponding sides of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are BC = 9.1cm and EF = 6.5cm. If the perimeter of ΔDEF is 25cm, find the perimeter of ΔABC.
In the given figure, ∠ABC = 90° and BD⊥AC. If AB = 5.7cm, BD = 3.8cm and CD = 5.4cm, find BC.
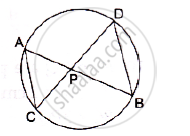
In a circle, two chords AB and CD intersect at a point P inside the circle. Prove that
(a) ΔPAC ∼PDB (b) PA. PB= PC.PD
In the given figure, A – D – C and B – E – C seg DE || side AB If AD = 5, DC = 3, BC = 6.4 then Find BE.

If Δ ABC , MN || BC .
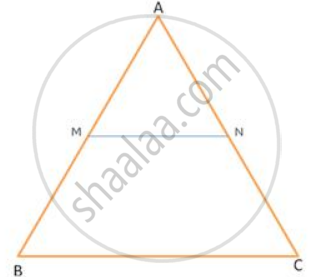
If AN : AC= 5 : 8, find ar(Δ AMN) : ar(Δ ABC)
In Δ PQR, MN is drawn parallel to QR. If PM = x, MQ = (x-2), PN = (x+2) and NR = (x-1), find the value of x.
A triangle LMN has been reduced by scale factor 0.8 to the triangle L' M' N'. Calculate: the length of M' N', if MN = 8 cm.
In a quadrilateral PQRS, the diagonals PR and QS intersect each other at the point T. If PT:TR = QT :TS = 1:2, show that ΔPTQ - DRTS
D and E are points on the sides AB and AC of ΔABC such that DE | | BC and divides ΔABC into two parts, equal in area. Find `"BD"/"AB"`.
The scale of a map is 1 : 50000. The area of a city is 40 sq km which is to be represented on the map. Find: The area of land represented on the map.
If ΔABC ~ ΔLMN and ∠B = 40°, then ∠M = ? Give reason.
In Quadrilateral ABCD, side AD || BC, diagonal AC and BD intersect in point P, then prove that `"AP"/"PD" = "PC"/"BP"`
Side of equilateral triangle PQR is 8 cm then find the area of triangle whose side is half of the side of triangle PQR.
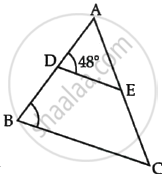
If ΔABC ∼ ΔDEF and ∠A = 48°, then ∠D = ______.
In figure, if AD = 6 cm, DB = 9 cm, AE = 8 cm and EC = 12 cm and ∠ADE = 48°. Find ∠ABC.