Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In ΔPQR, S and T are points on PQ and PR respectively. `(PS)/(SQ) = (PT)/(TR)` and ∠PST = ∠PRQ. Prove that PQR is an isosceles triangle.
Solution
Given `(PS)/(SQ) = (PT)/(TR)`
∠PST = ∠PRQ
To prove : PQR is an isosceles triangle
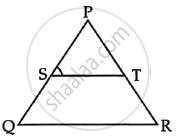
Proof : `(PS)/(SQ) = (PT)/(TR)`
∠PST = ∠PQR ...(Corresponding angles)
But ∠PST = ∠PRQ
∠PQR = ∠PRQ
PR = PQ ...(Sides opposite to equal angles are equal)
ΔPQR is isosceles triangle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In figure, `\frac{AO}{OC}=\frac{BO}{OD}=\frac{1}{2}` and AB = 5 cm. Find the value of DC.
Using Basic proportionality theorem, prove that a line drawn through the mid-points of one side of a triangle parallel to another side bisects the third side. (Recall that you have proved it in Class IX).
State, true or false:
All equiangular triangles are similar.
In the given figure, BC is parallel to DE. Area of triangle ABC = 25 cm2, Area of trapezium BCED = 24 cm2 and DE = 14 cm. Calculate the length of BC. Also, find the area of triangle BCD.
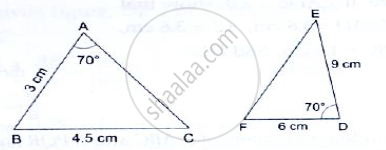
In each of the given pairs of triangles, find which pair of triangles are similar. State the similarity criterion and write the similarity relation in symbolic form:
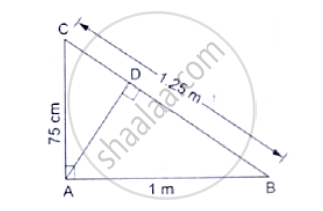
In the given figure, ∠CAB = 90° and AD⊥BC. Show that ΔBDA ~ ΔBAC. If AC = 75cm, AB = 1m and BC = 1.25m, find AD.
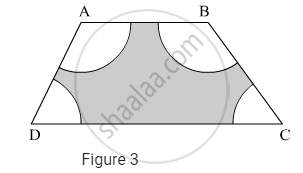
In Figure 3, ABCD is a trapezium with AB || DC, AB = 18 cm, DC = 32 cm and the distance between AB and DC is 14 cm. If arcs of equal radii 7 cm have been drawn, with centres A,B, C and D, then find the area of the shaded region.
In the given figure, X is any point in the interior of triangle. Point X is joined to vertices of triangle. Seg PQ || seg DE, seg QR || seg EF. Fill in the blanks to prove that, seg PR || seg DF.
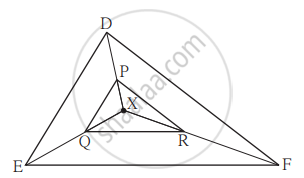
Proof : In ΔXDE, PQ || DE ...`square`
∴ `"XP"/square = square/"QE"` ...(I) (Basic proportionality theorem)
In ΔXEF, QR || EF ...`square`
∴ `square/square = square/square ..."(II)" square`
∴ `square/square = square/square` ...from (I) and (II)
∴ seg PR || seg DF ...(converse of basic proportionality theorem)
In the given figure, A – D – C and B – E – C seg DE || side AB If AD = 5, DC = 3, BC = 6.4 then Find BE.


O is any point in the interior of ΔABC. Bisectors of ∠AOB, ∠BOC and ∠AOC intersect side AB, side BC, side AC in
F, D and E respectively.
Prove that
BF × AE × CD = AF × CE × BD
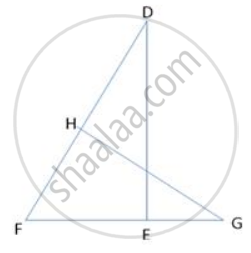
In figure , DEF is a right -angled triangle with ∠ E = 90 °.FE is produced to G and GH is drawn perpendicular to DE = 8 cm , DH = 8 cm ,DH = 6 cm and HF = 4 cm , find `("Ar" triangle "DEF")/("Ar" triangle "GHF")`
A ship is 400m laig and 100m wide. The length of its model is 20 cm. find the surface area of the deck of the model.
The actual area of an island is 1872km2 . On a map, this area is 117 cm2. if the length of the coastline is 44cm on the map, find the length of its actual coastline.
A model of an aeroplane is made to a scale of 1 : 400. Calculate : the length, in m, of the aeroplane, if length of its model is 16 cm.
In the following figure, point D divides AB in the ratio 3 : 5. Find :
BC = 4.8 cm, find the length of DE.
The given figure shows a parallelogram ABCD. E is a point in AD and CE produced meets BA produced at point F. If AE = 4 cm, AF = 8 cm and AB = 12 cm, find the perimeter of the parallelogram ABCD.
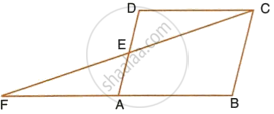
Find the area of the triangle ABC with the coordinates of A as (1, −4) and the coordinates of the mid-points of sides AB and AC respectively are (2, −1) and (0, −1).
In ΔABC, DE is parallel to BC and DE = 3:8.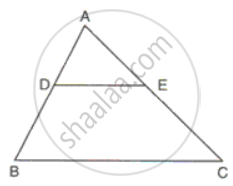
Find:
(i) AD : BD
(ii) AE, if AC = 16.
In ΔABC, point D divides AB in the ratio 5:7, Find: `"AD"/"AB"`
In ΔABC, BP and CQ are altitudes from B and C on AC and AB respectively. BP and CQ intersect at O. Prove that
(i) PC x OQ = QB x OP
(ii) `"OC"^2/"OB"^2 = ("PC" xx "PO")/("QB" xx "QO")`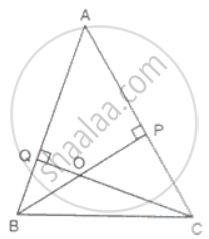
In the adjacent figure, ∆ABC is right angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE and hence find the lengths of AE and DE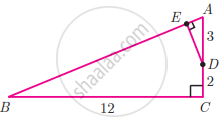
The perimeters of two similar triangles ∆ABC and ∆PQR are 36 cm and 24 cm respectively. If PQ = 10 cm, then the length of AB is
D is the mid point of side BC and AE ⊥ BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, ED = x, AD = p and AE = h, prove that b2 = `"p"^2 + "a"x + "a"^2/4`
Two similar triangles will always have ________ angles
In a square of side 10 cm, its diagonal = ______.
Is the following statement true? Why? “Two quadrilaterals are similar, if their corresponding angles are equal”.
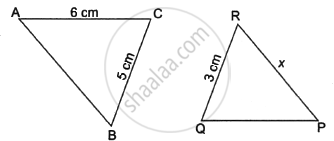
In the given figure, ΔABC ∼ ΔQPR, If AC = 6 cm, BC = 5 cm, QR = 3 cm and PR = x; them the value of x is ______.
ABCD is a parallelogram. Point P divides AB in the ratio 2:3 and point Q divides DC in the ratio 4:1. Prove that OC is half of OA.

