Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
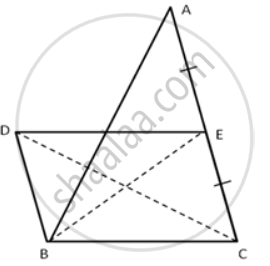
In the following figure, DE is parallel to BC.
Show that:
(i) Area ( ΔADC ) = Area( ΔAEB ).
(ii) Area ( ΔBOD ) = Area( ΔCOE ).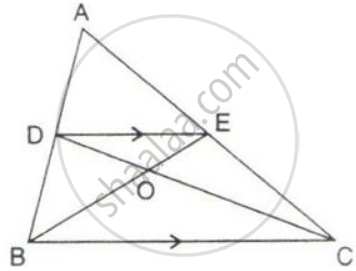
Solution
(i) In ΔABC, D is the midpoint of AB and E is the midpoint of AC.
`"AD"/"AB" = "AE"/"AC"`
DE is parallel to BC.
∴ A( ΔADC ) = A( ΔBDC ) = `1/2` A( ΔABC )
Again,
∴ A( ΔAEB ) = A( ΔBEC ) = `1/2` A( ΔABC )
From the above two equations, we have
Area( ΔADC ) = Area( ΔAEB ).
Hence Proved.
(ii) We know that the area of triangles on the same base and between the same parallel lines are equal.
Area( ΔDBC )= Area( ΔBCE )
Area( ΔDOB ) + Area( ΔBOC ) = Area( ΔBOC ) + Area( ΔCOE )
So, Area( ΔDOB ) = Area( ΔCOE ).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the given figure, if the area of triangle ADE is 60 cm2, state, given reason, the area of :
(i) Parallelogram ABED;
(ii) Rectangle ABCF;
(iii) Triangle ABE.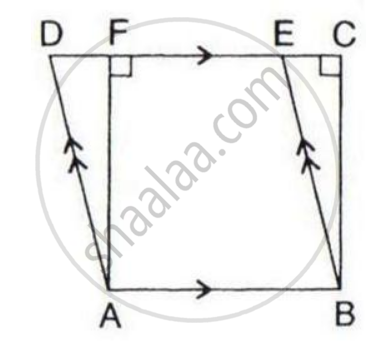
ABCD is a trapezium with AB // DC. A line parallel to AC intersects AB at point M and BC at point N.
Prove that: area of Δ ADM = area of Δ ACN.
In the given figure, M and N are the mid-points of the sides DC and AB respectively of the parallelogram ABCD.
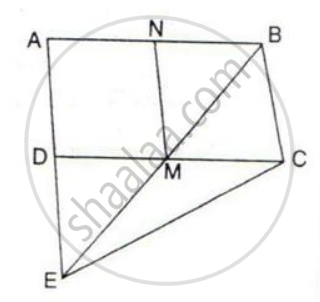
If the area of parallelogram ABCD is 48 cm2;
(i) State the area of the triangle BEC.
(ii) Name the parallelogram which is equal in area to the triangle BEC.
In the following figure, CE is drawn parallel to diagonals DB of the quadrilateral ABCD which meets AB produced at point E.
Prove that ΔADE and quadrilateral ABCD are equal in area.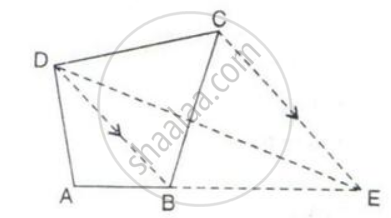
In the figure given alongside, squares ABDE and AFGC are drawn on the side AB and the hypotenuse AC of the right triangle ABC.
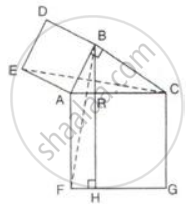
If BH is perpendicular to FG
prove that:
- ΔEAC ≅ ΔBAF
- Area of the square ABDE
- Area of the rectangle ARHF.
ABCD is a parallelogram a line through A cuts DC at point P and BC produced at Q. Prove that triangle BCP is equal in area to triangle DPQ.
ABCD is a parallelogram in which BC is produced to E such that CE = BC and AE intersects CD at F.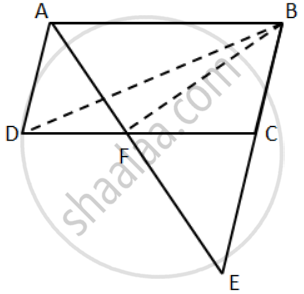
If ar.(∆DFB) = 30 cm2; find the area of parallelogram.
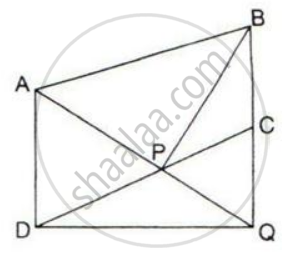
ABCD is a parallelogram. P and Q are the mid-points of sides AB and AD respectively.
Prove that area of triangle APQ = `1/8` of the area of parallelogram ABCD.
In the given figure, the diagonals AC and BD intersect at point O. If OB = OD and AB//DC,
show that:
(i) Area (Δ DOC) = Area (Δ AOB).
(ii) Area (Δ DCB) = Area (Δ ACB).
(iii) ABCD is a parallelogram.
In the following figure, BD is parallel to CA, E is mid-point of CA and BD = `1/2`CA
Prove that: ar. ( ΔABC ) = 2 x ar.( ΔDBC )