Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Kirchhoff’s junction rule is a reflection of ______.
- conservation of current density vector.
- conservation of charge.
- the fact that the momentum with which a charged particle approaches a junction is unchanged (as a vector) as the charged particle leaves the junction.
- the fact that there is no accumulation of charges at a junction.
Options
b and c
a and c
b and d
c and d
Solution
b and d
Explanation:
Junction rule: At any junction, the sum of the currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving the junction.
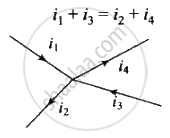
Or
Algebraic sum of the currents flowing towards any point in an electric network is zero, i.e., charges are conserved in an electric network.
The proof of this rule follows from the fact that when currents are steady, there is no accumulation of charges at any junction or at any point in a line. Thus, the total current flowing in, (which is the rate at which charge flows into the junction), must equal the total current flowing out.
Kirchhoff's junction rule is also known as Kirchhoff’s current law.
So, Kirchhoff's junction rule is the reflection of conservation of charge
Important point: Sign convention of current from a junction: We are taking outgoing current from a junction as negative. And we are taking incoming current towards a junction as positive.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
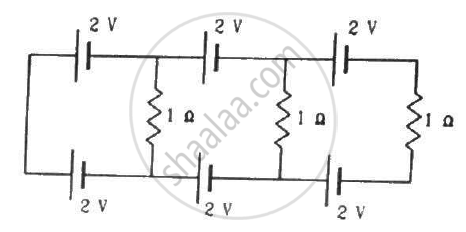
Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
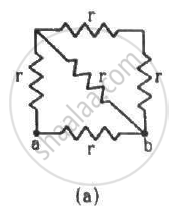
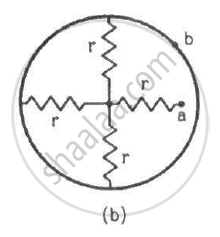
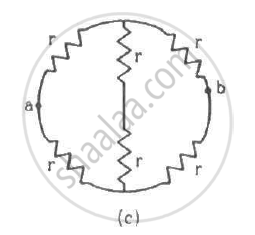
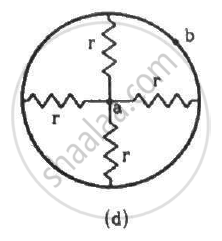
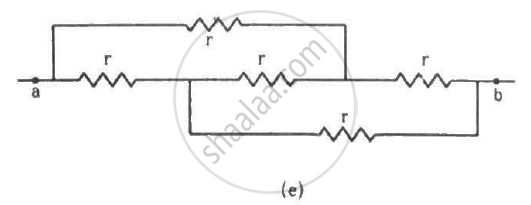
Find the equivalent resistances of the networks shown in the figure between the points a and b.
Consider the potentiometer circuit as arranged in the figure. The potentiometer wire is 600 cm long. (a) At what distance from the point A should the jockey touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? (b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance of 560 cm from A, what will be the current in the galvanometer?
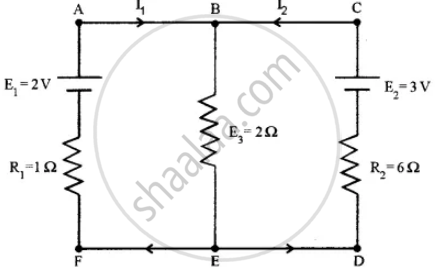
In the circuit shown in the figure below, E1 and E2 are two cells having emfs 2 V and 3 V respectively, and negligible internal resistance. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, find the values of currents l1 and I2.
Twelve wires each having a resistance of 3 Ω are connected to form a cubical network. A battery of 10 V and negligible internal resistance is connected across the diagonally opposite corners of this network. Determine its equivalent resistance and the current along each edge of the cube.
The e.m.f of The battery in a thermocouple is doubled. The rate of heat generated at one of the junction will.
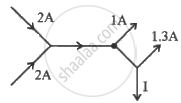
The figure below shows current in a part of electric circuit. The current I is ______.