Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve each of the following inequations graphically using XY-plane:
5y - 12 ≥ 0
Solution
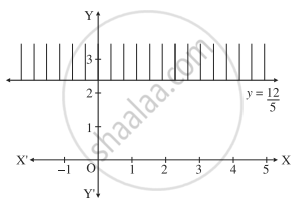
Consider the line whose equation is 5y - 12 ≥ 0 i.e. y = `12/5`
This represents a line parallel to X-axis passing3through the point `(0, 12/5)`
Draw the line y = `12/5`
To find the solution set, we have to check the position of the origin (0, 0).
When y = 0, 5y - 12 = 5(0) - 12 = - 12 > 0
∴ the coordinates of the origin does not satisfy the given inequality.
∴ the solution set consists of the line y = `12/5` and the non-origin side of the line which is shaded in the graph.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the feasible solution of the following inequation:
2x + 3y ≤ 6, x + y ≥ 2, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A manufacturing firm produces two types of gadgets A and B, which are first processed in the foundry and then sent to the machine shop for finishing. The number of man-hours of labour required in each shop for production of A and B per unit and the number of man-hours available for the firm is as follows :
| Gadgets | Foundry | Machine shop |
| A | 10 | 5 |
| B | 6 | 4 |
| Time available (hour) | 60 | 35 |
Profit on the sale of A is ₹ 30 and B is ₹ 20 per units. Formulate the L.P.P. to have maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of chemicals Aand B. Each chemical requires two types of raw material P and Q. The table below shows number of units of P and Q required to manufacture one unit of A and one unit of B and the total availability of P and Q.
| Chemical→ | A | B | Availability |
| Raw Material ↓ | |||
| P | 3 | 2 | 120 |
| Q | 2 | 5 | 160 |
The company gets profits of ₹ 350 and ₹ 400 by selling one unit of A and one unit of B respectively. (Assume that the entire production of A and B can be sold). How many units of the chemicals A and B should be manufactured so that the company gets a maximum profit? Formulate the problem as LPP to maximize profit.
The company makes concrete bricks made up of cement and sand. The weight of a concrete brick has to be at least 5 kg. Cement costs ₹ 20 per kg and sand costs of ₹ 6 per kg. Strength consideration dictates that a concrete brick should contain minimum 4 kg of cement and not more than 2 kg of sand. Form the L.P.P. for the cost to be minimum.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize z = 11x + 8y, subject to x ≤ 4, y ≤ 6, x + y ≤ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize z = 7x + 11y, subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
The point of which the maximum value of x + y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 70, 2x + y ≤ 95, x, ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is is obtained at ______.
If the corner points of the feasible solution are (0, 10), (2, 2) and (4, 0), then the point of minimum z = 3x + 2y is ______.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 4x + 2y subject to 3x + y ≤ 27, x + y ≤ 21, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 4x1 + 3x2 subject to
3x1 + x2 ≤ 15, 3x1 + 4x2 ≤ 24, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP:
Minimize z = 4x + 2y
Subject to 3x + y ≥ 27, x + y ≥ 21, x + 2y ≥ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A company produces mixers and food processors. Profit on selling one mixer and one food processor is Rs 2,000 and Rs 3,000 respectively. Both the products are processed through three machines A, B, C. The time required in hours for each product and total time available in hours per week on each machine arc as follows:
| Machine | Mixer | Food Processor | Available time |
| A | 3 | 3 | 36 |
| B | 5 | 2 | 50 |
| C | 2 | 6 | 60 |
How many mixers and food processors should be produced in order to maximize the profit?
A firm manufacturing two types of electrical items A and B, can make a profit of ₹ 20 per unit of A and ₹ 30 per unit of B. Both A and B make use of two essential components a motor and a transformer. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 2 transformers and each units of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of components per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. How many units of A and B should be manufactured per month to maximize profit? How much is the maximum profit?
Objective function of LPP is ______.
Choose the correct alternative :
Of all the points of the feasible region the optimal value of z is obtained at a point
Choose the correct alternative :
The corner points of the feasible region given by the inequations x + y ≤ 4, 2x + y ≤ 7, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, are
If the corner points of the feasible region are (0, 0), (3, 0), (2, 1) and `(0, 7/3)` the maximum value of z = 4x + 5y is ______.
State whether the following is True or False :
Saina wants to invest at most ₹ 24000 in bonds and fixed deposits. Mathematically this constraints is written as x + y ≤ 24000 where x is investment in bond and y is in fixed deposits.
Maximize z = 5x + 2y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 15, 5x + 2y ≤ 10, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize z = 7x + 11y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the Linear Programming problem graphically:
Maximize z = 3x + 5y subject to x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 also find the maximum value of z.
Choose the correct alternative:
Z = 9x + 13y subjected to constraints 2x + 3y ≤ 18, 2x + y ≤ 10, 0 ≤ x, y was found to be maximum at the point
The variables involved in LPP are called ______
A company produces two types of products say type A and B. Profits on the two types of product are ₹ 30/- and ₹ 40/- per kg respectively. The data on resources required and availability of resources are given below.
| Requirements | Capacity available per month | ||
| Product A | Product B | ||
| Raw material (kgs) | 60 | 120 | 12000 |
| Machining hours/piece | 8 | 5 | 600 |
| Assembling (man hours) | 3 | 4 | 500 |
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit.
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 2x2 subject to the constraints 5x1 + x2 ≥ 10; x1 + x2 ≥ 6; x1 + 4x2 ≥ 12 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
Solve the following linear programming problems by graphical method.
Minimize Z = 20x1 + 40x2 subject to the constraints 36x1 + 6x2 ≥ 108; 3x1 + 12x2 ≥ 36; 20x1 + 10x2 ≥ 100 and x1, x2 ≥ 0.
A firm manufactures pills in two sizes A and B. Size A contains 2 mgs of aspirin, 5 mgs of bicarbonate and 1 mg of codeine. Size B contains 1 mg. of aspirin, 8 mgs. of bicarbonate and 6 mgs. of codeine. It is found by users that it requires at least 12 mgs. of aspirin, 74 mgs. of bicarbonate and 24 mgs. of codeine for providing immediate relief. It is required to determine the least number of pills a patient should take to get immediate relief. Formulate the problem as a standard LLP.
The LPP to maximize Z = x + y, subject to x + y ≤ 1, 2x + 2y ≥ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 has ________.
The values of θ satisfying sin7θ = sin4θ - sinθ and 0 < θ < `pi/2` are ______
Which of the following can be considered as the objective function of a linear programming problem?
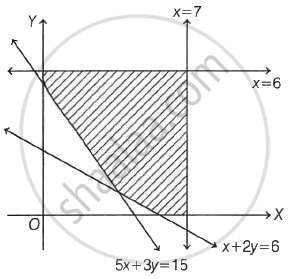
For the following shaded region, the linear constraint are:
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 7x + 11y, subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
