Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Sound waves from a loudspeaker spread nearly uniformly in all directions if the wavelength of the sound is much larger than the diameter of the loudspeaker. (a)Calculate the frequency for which the wavelength of sound in air is ten times the diameter of the speaker if the diameter is 20 cm. (b) Sound is essentially transmitted in the forward direction if the wavelength is much shorter than the diameter of the speaker. Calculate the frequency at which the wavelength of the sound is one tenth of the diameter of the speaker described above. Take the speed of sound to be 340 m/s.
Solution
Given:
The diameter of the loudspeaker is 20 cm.
Velocity of sound in air v = 340 m/s
As per the question,
wavelength (λ) of the sound is 10 times the diameter of the loudspeaker.
∴ (λ) = 20 cm \[\times 10\]= 200 cm = 2 m
(a) Frequency f = ?
As we know, \[v = f\lambda\]
\[\therefore f = \frac{v}{\lambda} = \frac{340}{2} = 170 Hz\]
(b) Here, wavelength is one tenth of the diameter of the loudspeaker.
⇒ λ = 2 cm = 2 × 10−2 m
\[\therefore f = \frac{v}{\lambda} = \frac{340}{2 \times {10}^{- 2}} = 17, 000 \text{ Hz } = 17 \text{ kHz }\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
Two tuning forks vibrate with the same amplitude but the frequency of the first is double the frequency of the second. Which fork produces more intense sound in air?
When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
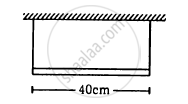
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
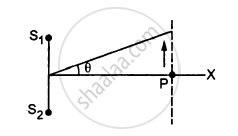
Two speakers S1 and S2, driven by the same amplifier, are placed at y = 1.0 m and y = −1.0 m(See figure). The speakers vibrate in phase at 600 Hz. A man stands at a point on the X-axis at a very large distance from the origin and starts moving parallel to the Y-axis. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1. (a) At what angle θ will the intensity of sound drop to a minimum for the first time? (b) At what angle will he hear a maximum of sound intensity for the first time? (c) If he continues to walk along the line, how many more can he hear?
A source of sound with adjustable frequency produces 2 beats per second with a tuning fork when its frequency is either 476 Hz of 480 Hz. What is the frequency of the tuning fork?
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats per second with a wire of length 25 cm vibrating in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the length is slightly shortened. What could be the minimum length by which the wire we shortened so that it produces no beats with the tuning fork?
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
A car moves with a speed of 54 km h−1 towards a cliff. The horn of the car emits sound of frequency 400 Hz at a speed of 335 m s−1. (a) Find the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn in front of the car. (b) Find the wavelength of the wave reflected from the cliff. (c) What frequency does a person sitting in the car hear for the reflected sound wave? (d) How many beats does he hear in 10 seconds between the sound coming directly from the horn and that coming after the reflection?
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
A transverse wave is represented by y = 2sin (ωt - kx) cm. The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity, will be ______.
