Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State conservation of angular momentum.
Solution
The law of conservation of angular momentum states that when no external torque acts on the body the net angular momentum of a rotating rigid body remains constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken.
A heavy particle of mass m falls freely near the earth's surface. What is the torque acting on this particle about a point 50 cm east to the line of motion? Does this torque produce any angular acceleration in the particle?
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis though the pivot. A horizontal force F is applied on the free end in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The quantities, that do not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are ________________ .
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
A particle of mass 5 units is moving with a uniform speed of v = `3sqrt 2` units in the XOY plane along the line y = x + 4. Find the magnitude of angular momentum
Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speed ω2 and ω2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident.
- Does the law of conservation of angular momentum apply to the situation? why?
- Find the angular speed of the two-disc system.
- Calculate the loss in kinetic energy of the system in the process.
- Account for this loss.
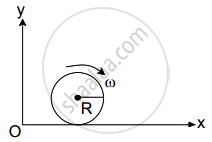
A spherical shell of 1 kg mass and radius R is rolling with angular speed ω on horizontal plane (as shown in figure). The magnitude of angular momentum of the shell about the origin O is `a/3 R^2` ω. The value of a will be:
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
