Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The chords corresponding to congruent arcs of a circle are congruent. Prove the theorem by completing following activity.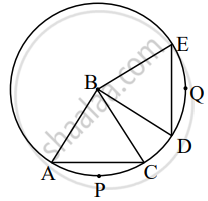
Given: In a circle with centre B
arc APC ≅ arc DQE
To Prove: Chord AC ≅ chord DE
Proof: In ΔABC and ΔDBE,
side AB ≅ side DB ......`square`
side BC ≅ side `square` .....`square`
∠ABC ≅ ∠DBE ......[Measure of congruent arcs]
∆ABC ≅ ∆DBE ......`square`
Solution
In ΔABC and ΔDBE,
side AB ≅ side DB ......[Radii of the same circle]
side BC ≅ side BE .....[Radii of the same circle]
∠ABC ≅ ∠DBE ......[Measure of congruent arcs]
∴ ∆ABC ≅ ∆DBE ......[SAS test of congruency]
∴ chord AC ≅ chord DE ......[Corresponding sides of congruent triangles]
RELATED QUESTIONS
Seg RM and seg RN are tangent segments of a circle with centre O. Prove that seg OR bisects ∠MRN as well as ∠MON with the help of activity.
In the given figure, the circles with centres A and B touch each other at E. Line l is a common tangent which touches the circles at C and D respectively. Find the length of seg CD if the radii of the circles are 4 cm, 6 cm. 
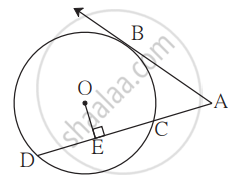
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle and B is a point of contact. seg OE ⊥ seg AD, AB = 12, AC = 8, find (1) AD (2) DC (3) DE.
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
Length of a tangent segment drawn from a point which is at a distance 12.5 cm from the centre of a circle is 12 cm, find the diameter of the circle.
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
Seg XZ is a diameter of a circle. Point Y lies in its interior. How many of the following statements are true ? (i) It is not possible that ∠XYZ is an acute angle. (ii) ∠XYZ can’t be a right angle. (iii) ∠XYZ is an obtuse angle. (iv) Can’t make a definite statement for measure of ∠XYZ.
In the given figure, M is the centre of the circle and seg KL is a tangent segment.
If MK = 12, KL = \[6\sqrt{3}\] then find –
(1) Radius of the circle.
(2) Measures of ∠K and ∠M.
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Seg AB, seg AC are tangent segments. Radius of the circle is r and l(AB) = r, Prove that ▢ABOC is a square. 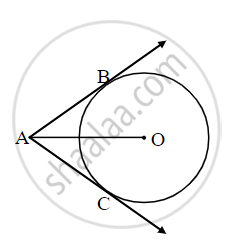
Proof: Draw segment OB and OC.
l(AB) = r ......[Given] (I)
AB = AC ......[`square`] (II)
But OB = OC = r ......[`square`] (III)
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
AB = `square` = OB = OC = r
∴ Quadrilateral ABOC is `square`
Similarly, ∠OBA = `square` ......[Tangent Theorem]
If one angle of `square` is right angle, then it is a square.
∴ Quadrilateral ABOC is a square.
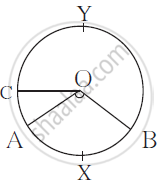
In the following figure ‘O’ is the centre of the circle.
∠AOB = 1100, m(arc AC) = 450.
Use the information and fill in the boxes with proper numbers.
(i) m(arcAXB) =
(ii)m(arcCAB) =
(iv)∠COB =
(iv)m(arcAYB) =
The perpendicular height of a cone is 12 cm and its slant height is 13 cm. Find the radius of the base of the cone.
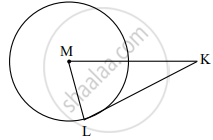
In the given figure, M is the centre of the circle and seg KL is a tangent segment. L is a point of contact. If MK = 12, KL = `6sqrt3`, then find the radius of the circle.
Prove the following theorem:
Tangent segments drawn from an external point to the circle are congruent.
Segment DP and segment DQ are tangent segments to the circle with center A. If DP = 7 cm. So find the length of the segment DQ.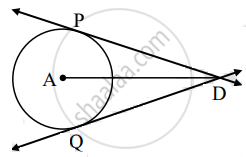
Length of a tangent segment drawn from a point which is at a distance 15 cm from the centre of a circle is 12 cm, find the diameter of the circle?
Tangent segments drawn from an external point to a circle are congruent, prove this theorem. Complete the following activity.
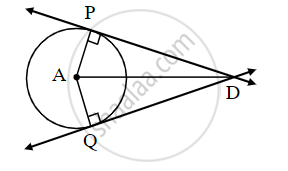
Given: `square`
To Prove: `square`
Proof: Draw radius AP and radius AQ and complete the following proof of the theorem.
In ∆PAD and ∆QAD,
seg PA ≅ `square` .....[Radii of the same circle]
seg AD ≅ seg AD ......[`square`]
∠APD ≅ ∠AQD = 90° .....[Tangent theorem]
∴ ∆PAD ≅ ∆QAD ....[`square`]
∴ seg DP ≅ seg DQ .....[`square`]
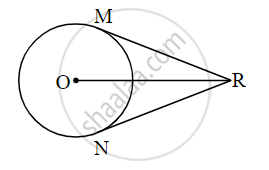
In the adjoining figure, O is the center of the circle. From point R, seg RM and seg RN are tangent segments touching the circle at M and N. If (OR) = 10 cm and radius of the circle = 5 cm, then
(i) What is the length of each tangent segment?
(ii) What is the measure of ∠MRO?
(iii) What is the measure of ∠MRN?
Prove that, tangent segments drawn from an external point to the circle are congruent.
In a parallelogram ABCD, ∠B = 105°. Determine the measure of ∠A and ∠D.

A circle touches side BC at point P of the ΔABC, from outside of the triangle. Further extended lines AC and AB are tangents to the circle at N and M respectively. Prove that : AM = `1/2` (Perimeter of ΔABC)
